We’ve lived through chip shortages, crypto mining crazes, and price hikes due to scalpers. Chip shortages will probably continue in the coming years, but at least we don’t have to worry about miners and scalpers so much because GPU crypto mining is essentially dead as of Q3 2022. So, is it a good time to upgrade your GPU? I think so.
Not everyone has the means to purchase a top-of-the-line GPU. So, what’s left? You can turn to entry-level or mid-range GPUs such as the RTX 3050 and the RTX 3060. Both are part of the RTX 30 series, so there is no doubt that they are great cards. In this 3050 vs 3060 comparison, I’ll walk you through why I think the RTX 3060 is the better choice.
3050 vs 3060 – Quick Comparison
| RTX 3050 | Specs | RTX 3060 |
|---|---|---|
| GA106-150-KA-A1 | GPU | GA106-300-A1 GA106-302 (LHR) |
| PCIe 4.0 x8 | Interface | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| 2,560 | CUDA Cores | 3,584 |
| 80 | TMUs | 112 |
| 80 | Tensor Cores | 112 |
| 20 | RT Cores | 28 |
| 1,552 MHz | Base Clock (Founders Edition) | 1,320 MHz |
| 1,777 MHz | Boost Clock (Founders Edition) | 1,777 MHz |
| 8 GB GDDR6 | Memory | 12 GB GDDR6 |
| 1,750 MHz (14 Gbps effective) | Memory Speed | 1,875 MHz (15 Gbps effective) |
| 224.0 GB/s | Bandwidth | 360.0 GB/s |
| 128-bit | Memory Bus | 192-bit |
| 130 W | TDP (Founders Edition) | 170 W |
| 300 W | Required PSU (Founders Edition) | 450 W |
| 68℃ (154.4℉) | Max Recorded Temp (Founder Edition) | 77℃ (170.6℉) |
| 42dB | Max Fan Noise (Founders Edition) | 46dB |
| 1x HDMI 2.1 3x DisplayPort 1.4a | Outputs | 1 x HDMI 2.1 3x DisplayPort 1.4a |
Nvidia GeForce RTX 3050
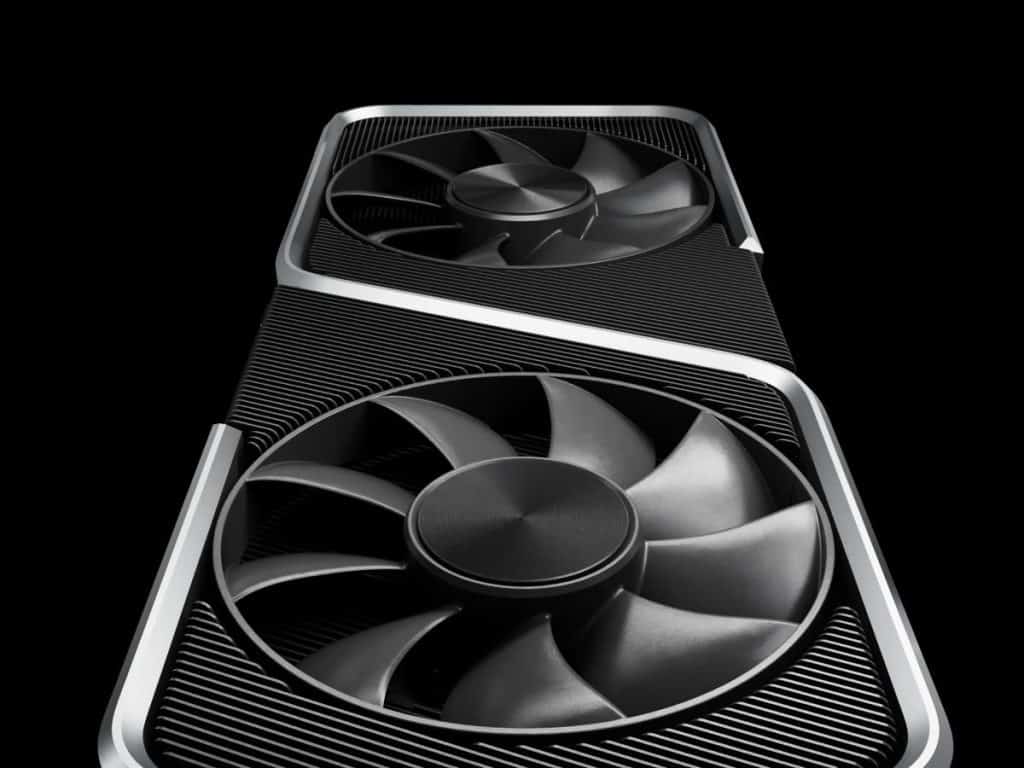

The Nvidia GeForce RTX 3050 is the only RTX 30 entry-level card. It was released in January 2022. It’s built on a PCIe x8 connection, features an 8 GB VRAM, and supports DirectX 12 Ultimate, ray tracing, and every game title currently available.
Pros:
- Lower price
- Lower TDP
- Less noisy
- Cheaper
Cons:
- Smaller PCIe connection
- Lower performance
Nvidia GeForce RTX 3060
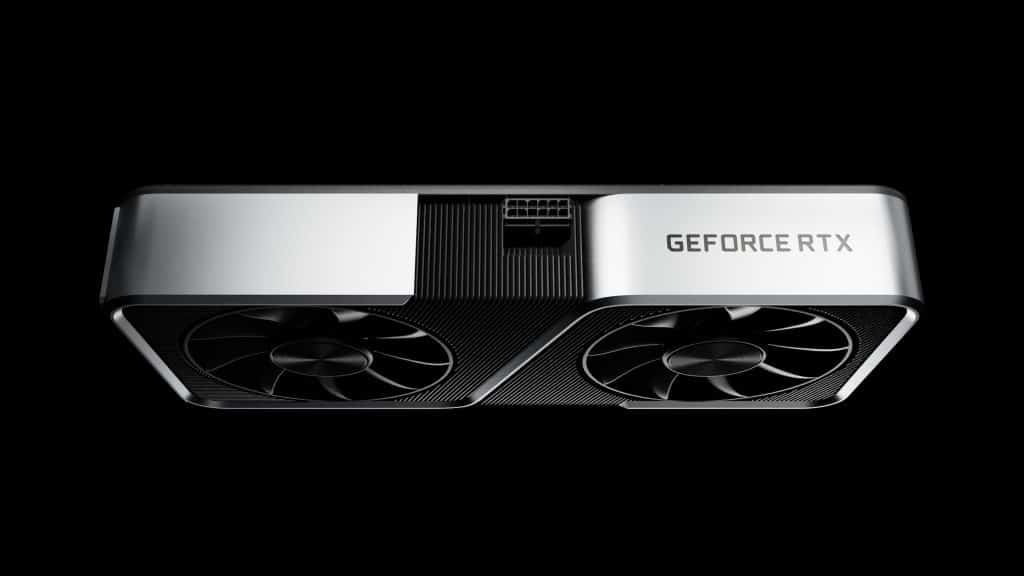

The Nvidia GeForce RTX 3060 is a mid-range card that features everything the 3050 has in higher numbers. More CUDA cores, more RT Cores, more Tensor Cores, more VRAM, and a PCIe x16 configuration. The RTX 3060 offers better performance than the RTX 3050 by 46%, according to users’ EFps tests.
Pros:
- Better performance
- Larger VRAM
- Faster VRAM
- More cores
Cons:
- Noisier
- Heats up more
Nvidia
Nvidia’s inception came from a successful prediction of the then almost non-existent gaming market’s expansion. It was the first company to develop a GPU in 1999. In 2015, it shifted its focus from the gaming industry toward research and development projects, many of which rely on Nvidia GPUs to run at all.
Key Specifications
Architecture
Ampere
Until the reveal of the RTX 40 series, Ampere was the fastest GPU architecture in the world. It features second-generation Ray Tracing Cores, third-generation Tensor Cores, and a few other bells and whistles, including Nvidia Broadcast.

While both the RTX 3050 and the 3060 are based on Ampere, the RTX 3050 is built on a PCIe x8 connection. This results in a certain amount of bottlenecking in performance-heavy titles.
Winner: Draw
Also Read: Differences between GTX and RTX Explained
Clock Speeds & Overclocking
Clock speeds are the operating frequency of GPUs, CPUs, RAM, and VRAM. Clock speeds are measured as “base” and “boost” clocks. This is not an exact science, and you’ll often see your card running below or above these speeds. It will idle at 300 MHz and will shoot beyond the boost clock whenever needed. Older titles won’t even hit the base clock to run optimally.
This is thanks to “dynamic clock speeds.” Clock speeds used to be static in older-generation cards, and we all had to resort to overclocking to achieve higher speeds, better graphics and game performance. You can overclock your card using dedicated software from Nvidia or third-party software such as MSI Afterburner.
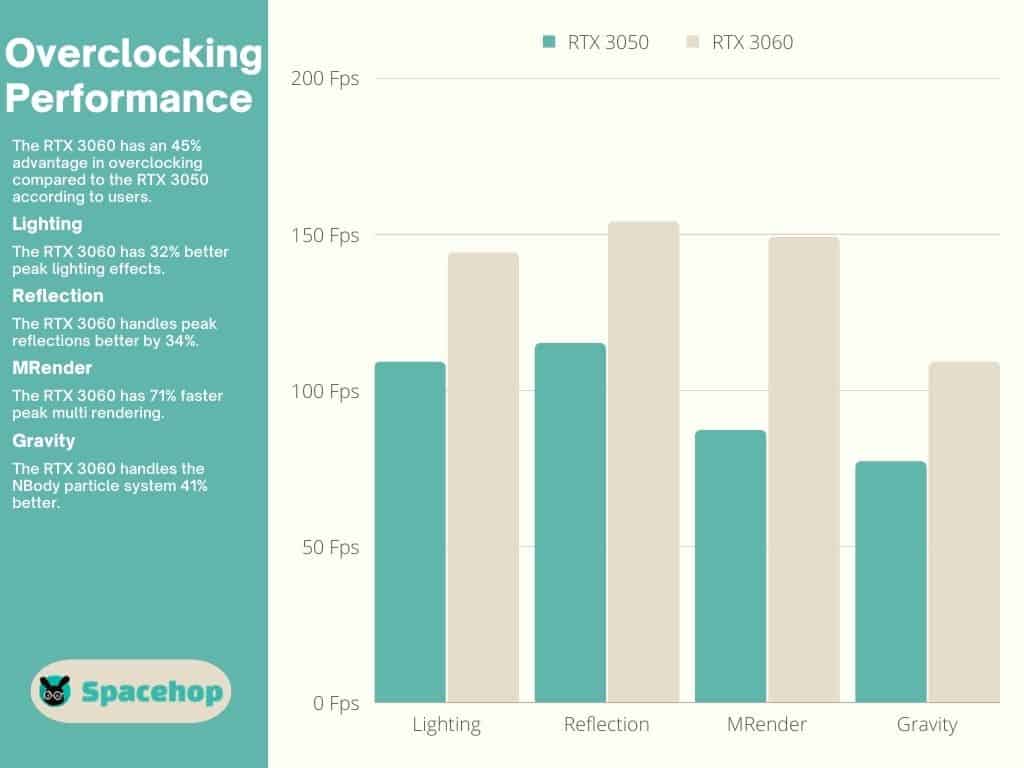
The RTX 3060 is the better overclocker, according to user tests, which gives it a 45% advantage in overclocking compared to the RTX 3050. Third-party variants offer even better results.
The RTX 3050 Founders Edition (FE) has a base clock of 1,552 MHz and a boost clock of 1,777 MHz. The RTX 3060 FE has a base clock of 1,320 MHz and a boost clock of 1,777 MHz. Third-party variants are often factory-overclocked, as you can see in the list below, where I’ve grouped the five best variants of each.
| Best RTX 3050 Variants | Boost Clock | Best RTX 3060 Variants | Boost Clock |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASUS ROG STRIX RTX 3050 GAMING OC | 1,860 MHz | ZOTAC RTX 3060 PGF XGOC | 1,897 MHz |
| Colorful iGame RTX 3050 Ultra W OC | 1,860 MHz | ASUS ROG STRIX RTX 3060 GAMING OC | 1,882 MHz |
| EVGA RTX 3050 XC | 1,845 MHz | ASUS ROG STRIX RTX 3060 V2 GAMING OC | 1,882 MHz |
| MSI RTX 3050 GAMING X | 1,845 MHz | EVGA RTX 3060 XC | 1,882 MHz |
| ASUS DUAL RTX 3050 OC | 1,822 MHz | EVGA RTX 3060 XC LHR | 1,882 MHz |
Winner: RTX 3060
Also Read: How to Undervolt your CPU and GPU
Cores Configuration
The main cores of Nvidia GPUs are called CUDA Cores, but that’s just a fancy name for the many cores in this type of parallel processor. The RTX 3050 has 2,560 CUDA Cores, and the RTX 3060 has 3,584. These cores are often counted as shaders because, on their own, they couldn’t achieve much without shaders.
Shaders
Shaders are generic programming languages that utilize GPU cores to create lights, shadows, characters, and many other aspects critical to 3D rendering. DirectX is probably the best-known shading language out there. Both cards use the same versions of each language because they’re from the same series. Nevertheless, the RTX 3060 has more cores that shaders can utilize.
| RTX 3050 | Shading Language | RTX 3060 |
|---|---|---|
| 12 Ultimate (12_2) | DirectX | 12 Ultimate (12_2) |
| 4.6 | OpenGL | 4.6 |
| 3.0 | OpenCL | 3.0 |
| 1.3 | Vulkan | 1.3 |
| 8.6 | CUDA | 8.6 |
| 6.6 | Shader Model | 6.6 |
Ray Tracing Cores
Another shading language is DirectX Raytracing, which was originally rolled out because of Nvidia’s Ray Tracing Cores. Ray tracing was previously only used in CGI movies to blend animated elements with real-life scenes. It mimics how light particles behave in the real world and transfers that behavior to the virtual world as best it can. Nvidia introduced real-time GPU ray tracing in the RTX 20 series.

Both the RTX 3050 and the 3060 feature second-generation RT Cores, though not many of them. The RTX 3050 has 20 RT Cores, and the 3060 has 28. Not enough to really handle ray tracing well in current titles, let alone future ones.
TMUs
Another critical part of your graphics card is how many Texture Mapping Units it has. As virtually every surface in a 3D space requires a texture to cover it, you can see why these are important. Long ago, TMUs, CUDA Cores, SMs, and ROPs were all featured equally in GPUs. Nowadays, they are decoupled from one another to achieve higher shader counts and better overall performance.
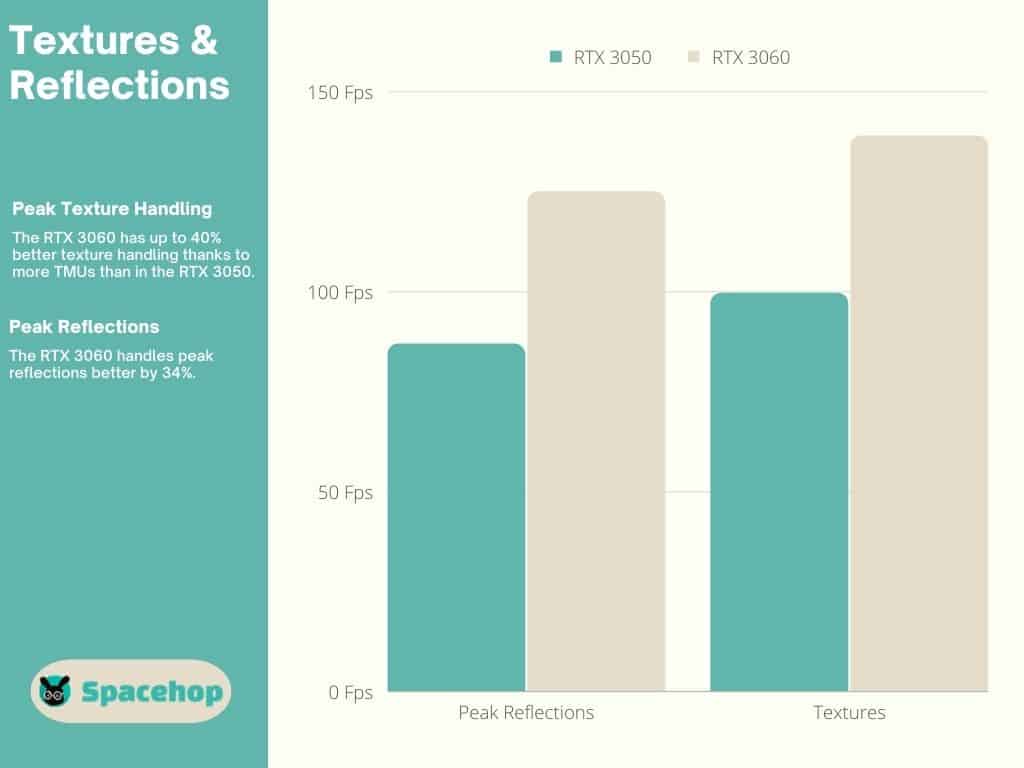
The RTX 3050 has 80 TMUs, while the 3060 has 112, over 40% more. The results are obvious as the RTX 3060 handles textures better by up to 40%.
Tensor Cores
Tensor Cores weren’t designed with gaming in mind. Their immense power was designed to power AI and machine learning development. In a sense, the entire RTX 30 series is a byproduct of Nvidia’s continued efforts to develop faster hardware to fuel advanced software development. Nevertheless, Nvidia wouldn’t have included them if they didn’t help out on your PC.

They give a massive boost in performance (Nvidia DLSS) and help project 3D images to your 2D screen, allow for higher frame rates without sacrificing image quality, and speed up calculations that handle scale, skew, rotation, and more. But you can double down and use them to create your own AI. Your choice.
Winner: RTX 3060
VRAM & Memory Specs
Both the RTX 3050 and the 3060 use GDDR6 VRAM. The 3050 has 8 GB paired with a 128-bit memory BUS, delivering an effective speed of 14 Gbps clocked at 1,750 MHz and a bandwidth of 224 GB/s. The RTX 3060 has a 50% larger VRAM of 12 GB paired with a 192-bit BUS, delivering an effective speed of 15 Gbps clocked at 1,875 MHz and a bandwidth of 360 GB/s.
Winner: RTX 3060
Also Read: VRAM versus RAM: What are the key differences?
Performance
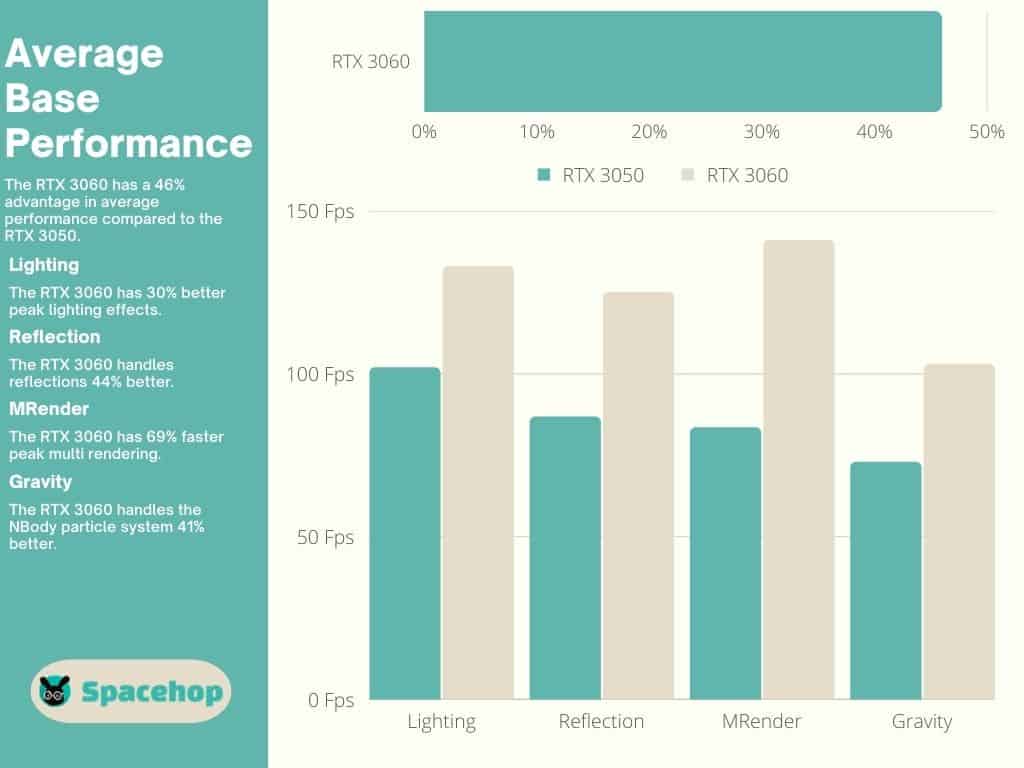
The RTX 3060 wins right off the bat in benchmark performance tests by 36%. That’s across all three HD resolutions (1080p, 1440p, 4K). User benchmark tests have it at a 46% advantage compared to the RTX 3050.
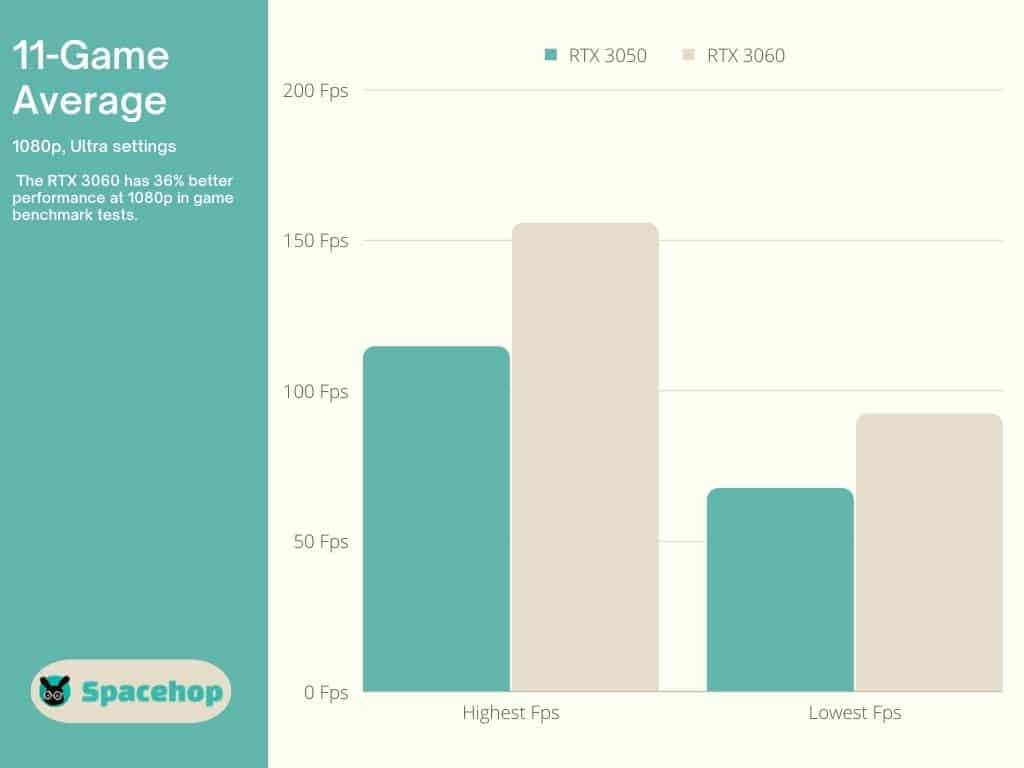
The GTX 3060 outperforms the RTX 3050 by 36% at 1080p.
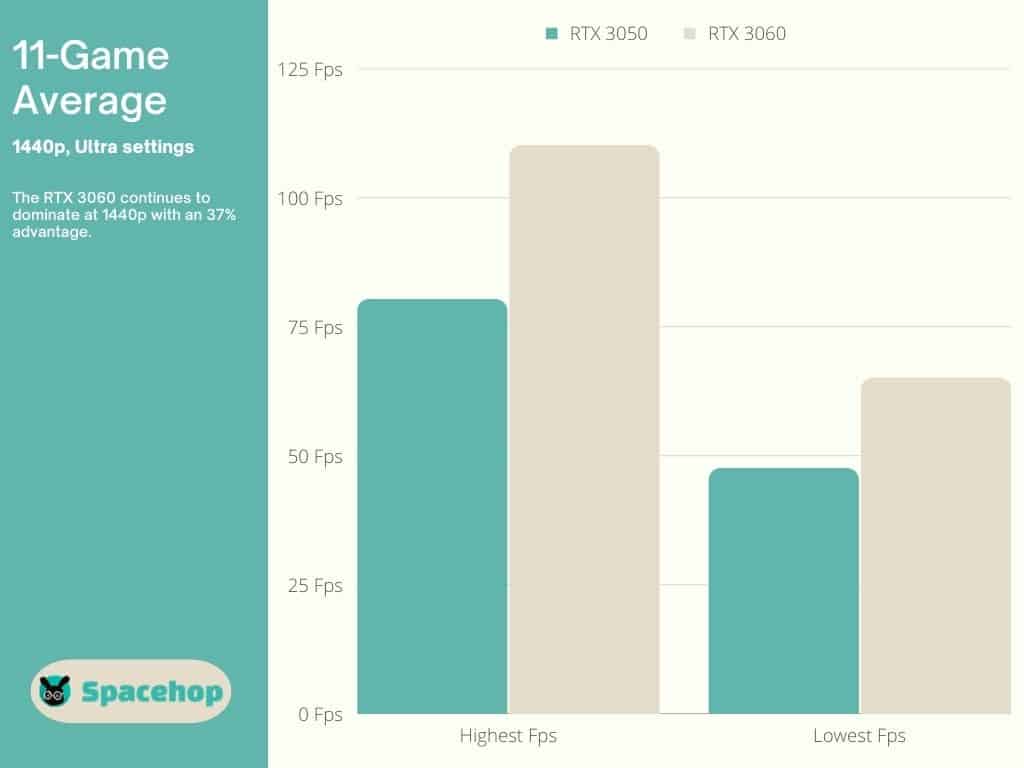
The GTX 3060 outperforms the RTX 3050 by 36.9% at 1440p.
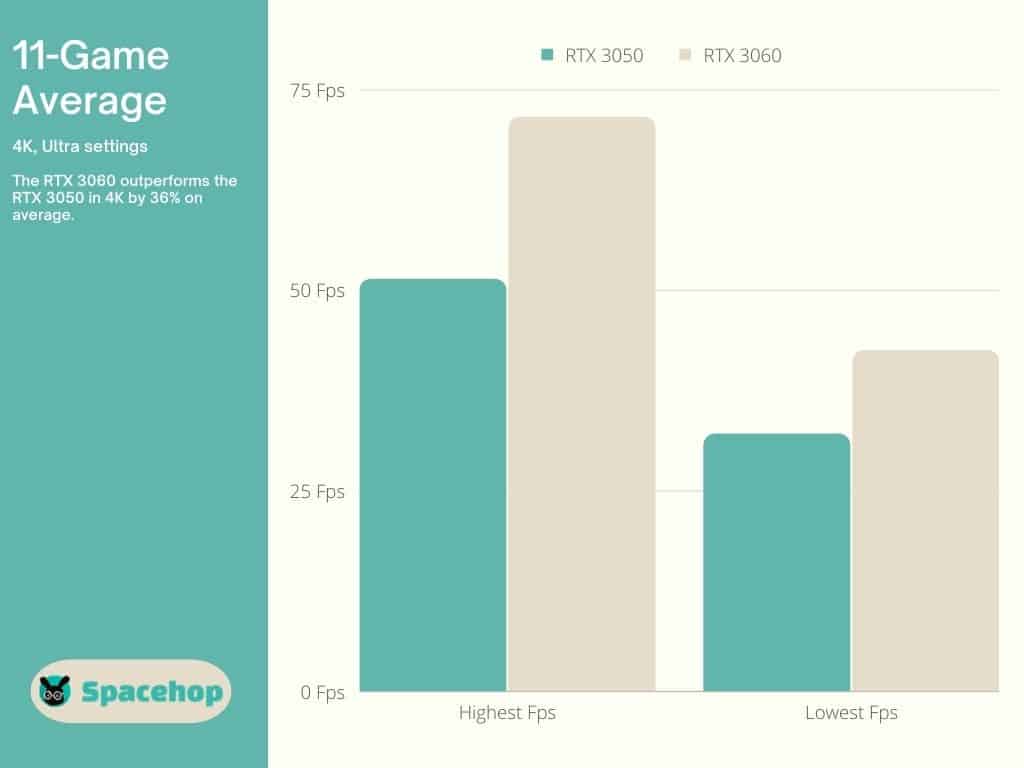
The GTX 3060 outperforms the RTX 3050 by 36% again at 4K.
Winner: RTX 3060
Also Read: 4K UHD vs 1080p Resolution – What’s the difference?
Connectivity
The FE variants of both cards offer the same output setup with one HDMI port and three DisplayPorts. Some third-party variants offer different setups, so read the fine print before purchasing. Both cards require a PSU connection for power. The 3050 uses an 8-pin connector, while the 3060 has the new 12-pin port, so you’ll need an 8 or 6-pin adapter depending on your PSU.
Winner: Draw
TDP
TDP represents two things: Thermal Design Power — how much power a subsystem is allowed to draw from your PSU; and Thermal Design Point — how much heat that subsystem is allowed to produce.
Neither of these cards is heavy on power usage, and most run-of-the-mill PSUs can power them. The 3050 has a TDP of 130 W and requires a 300W PSU. The 3060 has a TDP of 170 W requiring a 450W PSU.
The RTX 3060 proved to be the hotter card (literally) during testing. It hit 77℃ (170.6°F), while the RTX 3050 didn’t go above 68℃ (154.4°F). These are FE versions’ temperatures, and third-party variants will heat up more due to their overclocked settings.
Winner: RTX 3050
3050 vs 3060 – Pricing & Availability
The RTX 3050 FE was originally priced at $249 upon release. The RTX 3060 was priced at $329. Both were released during a global chip shortage and the following rise in GPU prices. Things have died down in the last couple of months, and prices are closer to what they were upon release.
I’ve found several good deals for the RTX 3050, all on sale currently, but none below MSRP. The cheapest deal I found is for a ZOTAC Gaming variant priced 19% above MSRP. You can grab an MSI Gaming 21% above currently. No.5 (Asus Dual) on the best-ever list is currently priced at 27% above. The ASUS ROG Strix (No.1 on our list) is priced 52% above MSRP.
The RTX 3060 is and always will be priced above the RTX 3050. An MSI Gaming variant goes for 15% above MSRP currently. These ZOTAC Gaming and GIGABYTE variants are priced at 17% above MSRP. This ASUS Dual variant is priced 24% above, while an ASUS TUF will set you back the most as it is priced 48% above MSRP.
*Prices and percentages may be different at the time of reading.
Conclusion
There is no doubt in my mind which card wins in this 3050 vs 3060 comparison. The RTX 3060 delivers much better performance (46%, according to users). It’s also a better investment in the long run because it has 50% more VRAM and more cores (be they CUDA, RT, or Tensor). I’d gladly pay the price difference for the RTX 3060, knowing I’m set for a longer time than I would be with the 3050.