Nvidia fans were anticipating the next GPU lineup from the company until recently, when the RTX 40 series was announced. Two cards were presented then, both top-tier. And I can safely say the pinnacle of Nvidia’s GPU evolution is the Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 (for now). Even with a reveal from the competition on November 3, the only real challenger to the RTX 40 series is Nvidia’s previous series.
This RTX 4090 vs RTX 3090 comparison is a walkthrough of everything you need to know regarding the RTX 4090 and how it compares to its predecessor or, to put it bluntly, how much better the 4090 is.
RTX 4090 vs RTX 3090 – Quick Comparison
| RTX 4090 | Specs | RTX 3090 |
|---|---|---|
| AD102-300-A1 | GPU Variant | GA102-300-A1 |
| PCIe 4.0 x16 | Interface | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| 16,384 | CUDA Cores | 10,496 |
| 512 | Tensor Cores | 328 |
| 512 | TMUs | 328 |
| 128 | RT Cores | 82 |
| 2,235 MHz | Base Clock (Founders Edition) | 1,395 MHz |
| 2,520 MHz | Boost Clock (Founders Edition) | 1,695 MHz |
| 24 GB GDDR6X | Memory | 24 GB GDDR6X |
| 1,313 MHz (21 Gbps effective) | Memory Speed | 1,219 MHz (19.5 Gbps effective) |
| 1,008 GB/s | Bandwidth | 936.2 GB/s |
| 384-bit | Memory Bus | 384-bit |
| 450 W | TDP (Founders Edition) | 350 W |
850 W | Required PSU (Founders Edition) | 750 W |
| 90℃ (194℉) | Maximum Temperature | 93℃ (199.4℉) |
| 72℃ (161.6℉) | Highest Recorded Temperature (Founders Edition) | 83℃ (181.4℉) |
| 48dB | Highest Recorded Noise (Founders Edition) | 49dB |
| 1x HDMI 2.13x DisplayPort 1.4a | Outputs (Founders Edition) | 1x HDMI 2.13x DisplayPort 1.4a |
| 1x 16-pin | Power Connectors (Founders Edition) | 1x 12-pin |
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090
Nvidia CEO, Jensen Huang, announced the RTX 40 series on September 20, 2022. The RTX 4090 became available less than a month later. Marketing aside, the 4090 is currently the best card on the market, even with RDNA 3 announced recently (was there any doubt?). But how does it compare to its own predecessor, the RTX 3090? Honestly, it blows it away.
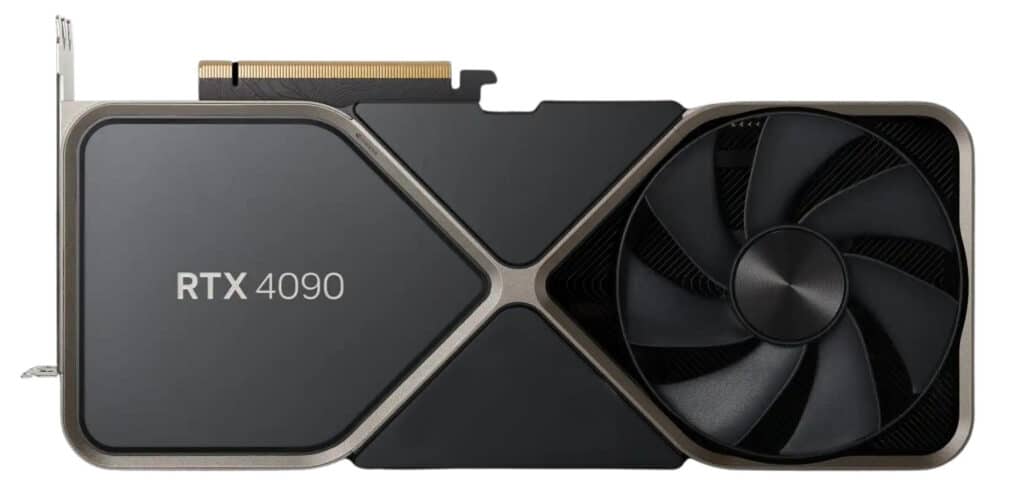

It has 56% more CUDA Cores and almost three times more transistors than the RTX 3090. It has the same 24 GB GDDR6X VRAM and next-generation Tensor and RT Cores. It offers roughly 86% better effective speed performance than the 3090, a card that is also a top-shelf performer.
Pros:
- Much better performance
- 24 GB VRAM
- Larger core configuration
- Higher clock speeds
Cons:
- Size
- Price
Nvidia GeForce RTX 3090
The GeForce RTX 3090 hit the market in Q3 2020, right after Nvidia announced the Ampere architecture. The 3090 and the 3090 Ti were the two best performers until Ada Lovelace. The 3090 has 10,496 CUDA Cores, a 24GB GDDR6X VRAM, and relatively low clock speeds compared to the RTX 40 series and Ampere’s direct competition, RDNA 2.
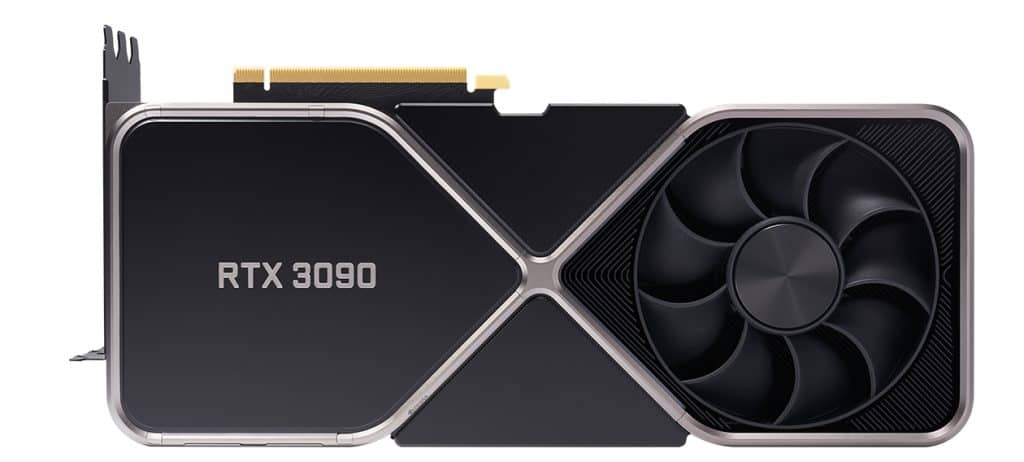

The RTX 3090 is an enthusiast-class graphics card. Its price was jaw-dropping from the beginning and has remained out of reach for many of us. The launch of the RTX 40 series brought a price drop for the 3090, and I expect that trend to continue.
Pros:
- Great performance
- 24 GB VRAM
- Lower price (on average)
- Lots of partner variants
Cons:
- Hotter
- Louder (Founders Edition)
Nvidia
Nvidia was the first company to ever release a GPU. The people over at Nvidia successfully predicted the expansion of the gaming industry and have since moved on to develop GPUs powerful enough to help advance AI research and development projects throughout the world.
Nvidia’s newest innovations catered toward AI development are also present in its consumer-grade GPUs, resulting in an immense performance advantage for the RTX 4090.
4090 vs 3090: Key Specifications
Architecture
Ada Lovelace
Nvidia releases a new RTX microarchitecture every two years. We got Turing in 2018, Ampere in 2020, and Ada Lovelace in 2022. Each was an impressive advancement upon its predecessors, with the final offering remarkable differences. Ada Lovelace offers five key innovations compared to Ampere.
- All-New 4nm Process Node
- Shader Execution Reordering
- DLSS 3.0
- Third-Gen Tensor Cores
- Improved Power and Efficiency

Nvidia switched from Samsung’s 8nm process to TSMC’s 4nm N4 technology, which is half as small as the previous-gen Ampere chip and delivers more power efficiency. GPUs are great because they use multiple cores to handle the same task. This is efficient when rendering regular scenes but falls short at ray tracing.
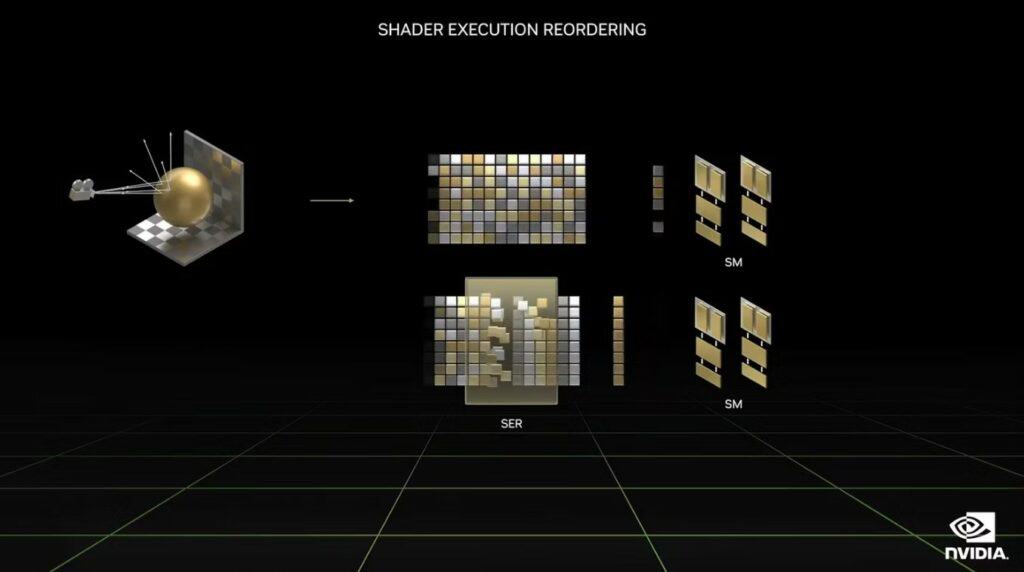
Shader Execution Reordering (SER) reschedules shader workloads, grouping and processing similar shaders together, resulting in more efficient streaming multiprocessors. This ensures more computing power for ray tracing and calculating every ray trajectory during rendering.
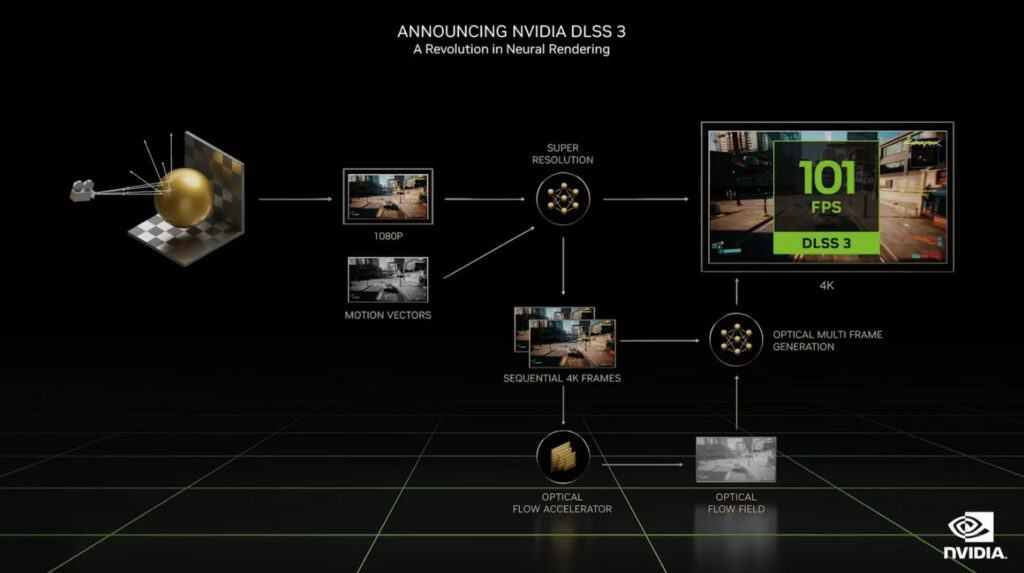
RTX draws a lot of your GPU’s resources, especially at 4K. To counter this, Nvidia created DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling). It reduces GPU workloads by predicting the next pixel using AI. DLSS 3.0 expands its predictions from pixels to entire frames without seeing the next unrendered image data.
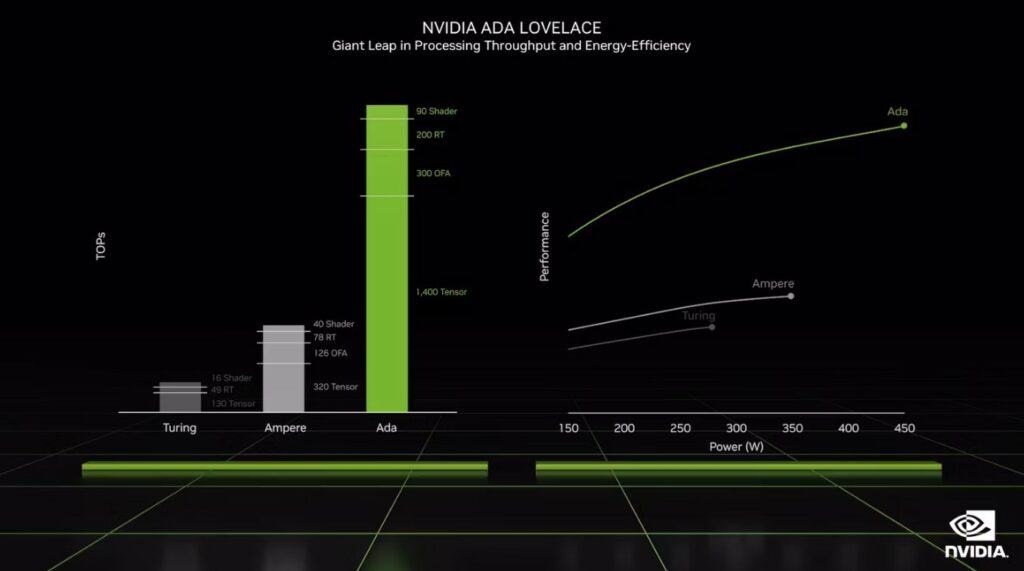
DLSS relies on Tensor Cores. Ada Lovelace features fourth-gen Tensor Cores that are more than four times faster than Ampere’s third-gen Tensor Cores. All of this results in twice the performance at the same power rating. This enables Ada Lovelace GPUs to endure overclocking beyond 3 GHz and even set world records.
Ampere
All of the above seems daunting, yet Ampere was a feat of its own. Ampere was an improvement upon its predecessor (Turing) as much as Ada Lovelace is upon it. Ampere’s RTX 3090 was second only to its Ti version until Ada. It has second-gen RT Cores and third-gen Tensor Cores and offers excellent performance.
Winner: RTX 4090
Also Read: Learn the difference between GTX and RTX series cards
Design and Build
The RTX 4090 Founders Edition (FE) is a triple-slot card. Most of its third-party variants (23 of 35) are quad-slot cards because a card this powerful creates a lot of heat, so Nvidia partners had to come up with some innovative cooling configurations. The smallest variants (dual-slot) are water-cooled, though you’ll have to make room for their double-fanned radiators within your case.
The RTX 3090 FE is a triple-slot card, as are most of its third-party variants. Of the 116 partner cards available, only four are quad-slot designs. Water-cooled variants feature single or dual-slot designs and are also a minority.
Winner: Draw
Cores Configuration
The most important part of a graphics card is its core configuration. The various core types used in GPUs were equal but have been decoupled to achieve scalability and modulation during production. This resulted in more main (CUDA) cores and fewer of the rest (TMUs, ROPs, SMs, etc.).
The RTX 4090 features 56% more CUDA Cores than the RTX 3090, even though it has a die size twice as small. It has 16,384 CUDA Cores and 76 billion transistors. The RTX 3090 has 10,496 CUDA Cores and 28 billion transistors. These “main” GPU cores are often counted as shaders because they require shaders (generic programming languages) to operate. Think of them as instructions.
Shaders
There are several shader languages that a GPU requires to operate. The most well-known shader is DirectX (if we had a nickel for every time we installed it). CUDA Cores require a specific shader known as CUDA. Ray tracing uses another shader — DirectX Raytracing which was integrated into the DirectX 12 Ultimate version used by both cards.
The RTX 4090 and the 3090 use the same shaders for the most part, except for the CUDA shader. Nvidia developed a new CUDA version for the RTX 40 series, CUDA 8.9. The RTX 30 series uses 8.6.
| RTX 4090 | Shader Language | RTX 3090 |
|---|---|---|
| 12 Ultimate (12_2) | DirectX | 12 Ultimate (12_2) |
| 4.6 | OpenGL | 4.6 |
| 3.0 | OpenCL | 3.0 |
| 1.3 | Vulkan | 1.3 |
| 8.9 | CUDA | 8.6 |
| 6.6 | Shader Model | 6.6 |
RT Cores

Nvidia introduced RT Cores in 2018 (Turing). The RTX 4090 features the third RT iteration offering much better ray tracing performance than the RTX 3090 and its second-gen RT Cores. Ray tracing uses a lot of computing power as it imitates real-life light particles and how they act, mimicking that behavior in virtual worlds.

So, the RTX 4090 has newer RT Cores, but it has another advantage. The RTX 4090 has 128 third-gen RT Cores, while the 3090 has only 82 second-gen RT Cores. Still, ray tracing is only available in a minor percentage of games presently, and we’re yet to see how much these cores will mean in the future. On the other hand, textures are omnipresent, and having enough TMUs (Texture Mapping Units) is essential.
TMUs
Virtually every surface in a 3D environment is covered by a texture of some sort. You can’t mistake a missing texture when you see it. The RTX 4090 has 512 TMUs compared to the RTX 3090’s 328 TMUs. Even though that’s just a 35% increase, the 4090 has up to 123% better texture handling.
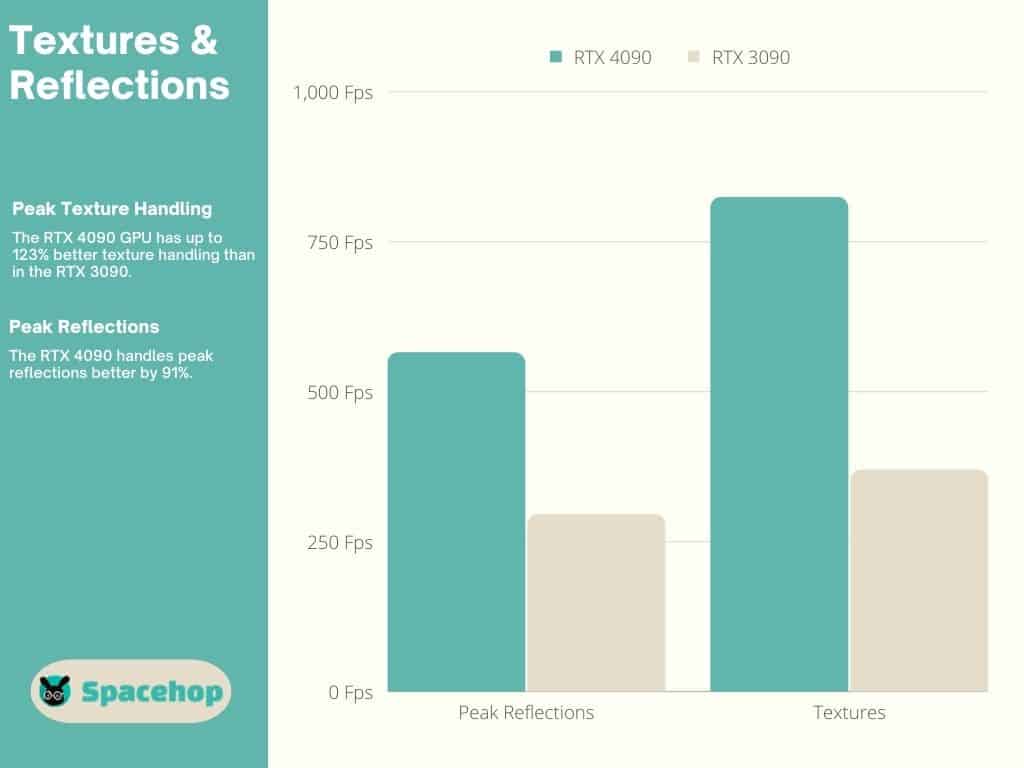
Tensor Cores
Nvidia invented Tensor Cores to tackle calculations required by AI development projects. They’re immensely powerful, especially the fourth-gen Tensor Cores used in the RTX 40 series. They’re responsible for DLSS, a technology that lightens the load on your GPU while greatly enhancing performance. The RTX 4090 has 512 Tensor Cores, and the RTX 3090 has 328.
Winner: RTX 4090
Clock Speeds & Overclocking
So Nvidia obviously boosted its core configuration in the RTX 40 series when compared to the RTX 30 series, but it did more than that. Personally, I thought the RTXX 30 series offered low clock speeds. Not to say that they weren’t enough, but it seemed like there was room to improve. I guess Nvidia thought so also because the RTX 40 series offers higher clock speeds than its predecessor.
Clock speeds are the operating frequency of a component such as a GPU. CPUs, RAM, and VRAM also have operating frequencies. Modern GPUs feature dynamic clock speeds, fluctuating between a base and boost clock speed. Before the introduction of dynamic clock speeds, GPUs had static speeds, and most of us were overclocking our cards to get some extra performance from them.
I see no need to overclock cards like this for everyday gaming. My card jumps beyond its official boost clock whenever needed without my intervention (overclocking) and drops below the base clock whenever I play an older title. There isn’t a title out there that either of these cards can’t handle with their default clock speeds.
The RTX 4090 has a base clock speed of 2,235 MHz and a boost clock of 2,560 MHz. Its most overclocked third-party variant (so far) has a boost clock of 2,640 MHz. The RTX 3090 has a base clock speed of 1,395 MHz and a boost clock speed of 1,695 MHz. Its most overclocked third-party variant has a boost clock of 1,920 MHz.
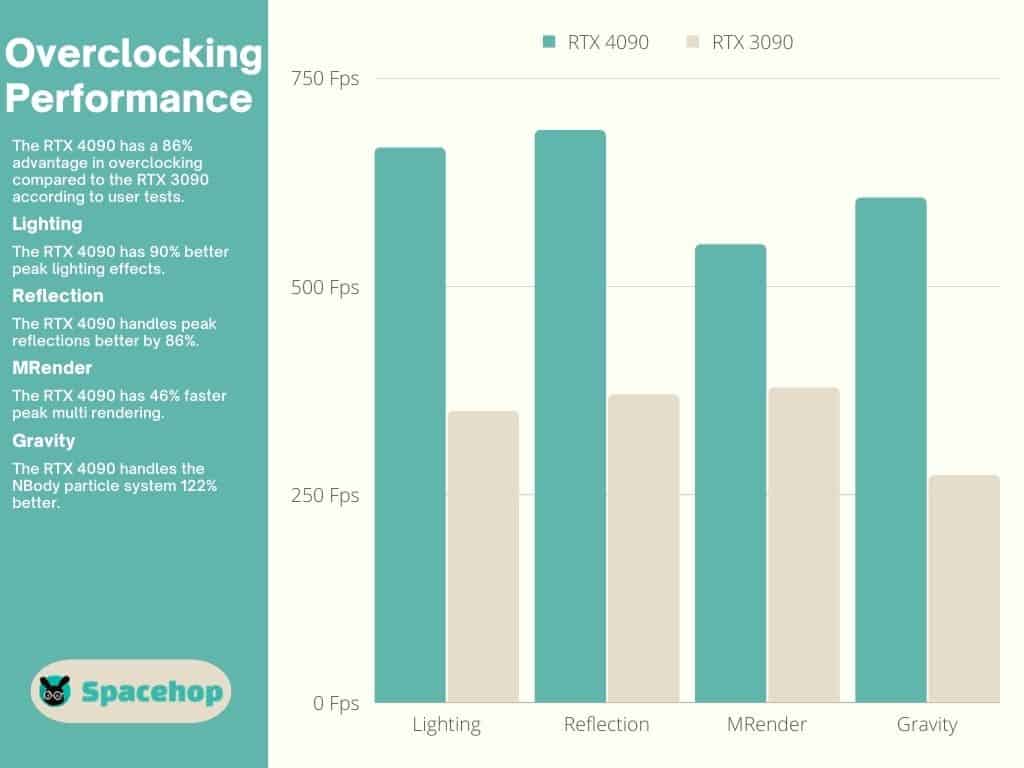
Many third-party cards are factory-overclocked, and the most powerful of both have water-cooling builds. If you are up for toying around with overclocking, you can use Nvidia Experience or any third-party software, such as MSI Afterburner. I strongly recommend you read our guide before attempting it.

| RTX 4090 | Boost Clock | RTX 3090 | Boost Clock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorful iGame RTX 4090 Neptune OC*1, 2 | 2,640 MHz | EVGA RTX 3090 KINGPIN*1, 2 | 1,920 MHz |
| Colorful iGame RTX 4090 Vulcan OC*3 | 2,625 MHz | EVGA RTX 3090 KINGPIN Hydro Copper*2, 5 | 1,920 MHz |
| MSI RTX 4090 SUPRIM LIQUID X*1, 2 | 2,625 MHz | ASUS ROG STRIX RTX 3090 GAMING OC*3 | 1,860 MHz |
| MSI RTX 4090 SUPRIM X*4 | 2,625 MHz | ASUS ROG STRIX RTX 3090 GUNDAM OC*3 | 1,860 MHz |
| ASUS ROG STRIX RTX 4090 GAMING OC*4 | 2,610 MHz | ASUS ROG STRIX RTX 3090 OC EVA Edition*3 | 1,860 MHz |
*1 – Dual-slot
*2 – Watercooled
*3 – Triple-slot
*4 – Quad-slot
*5 – Single-slot
Winner: RTX 4090
Also Read: Undervolting your CPU and GPU Safely
VRAM & Memory Specs
Another area in which Nvidia chose to up clock speeds is the VRAM. Both cards have the same 24GB GDDR6X configuration and use a 384-bit memory BUS. I guess this is the pinnacle of VRAM evolution for now. The difference, however slight, is in their clock speeds.
The RTX 4090’s VRAM is clocked at 1,313 MHz delivering an effective speed of 21 Gbps and a bandwidth of 1,008 GB/s. The RTX 3090’s VRAM is clocked at 1,219 MHz delivering an effective speed of 19.5 Gbps and a bandwidth of 936.2 GB/s.
Winner: RTX 4090
Also Read: Learn about the key differences between VRAM and RAM
Performance
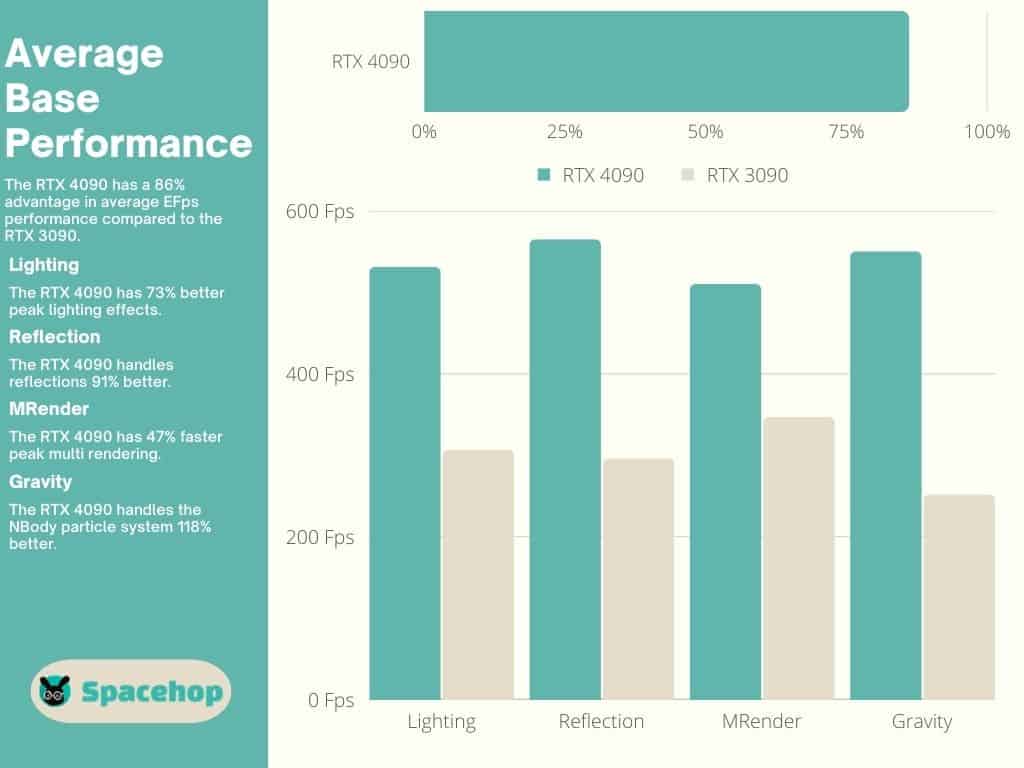
The RTX 3090 is a top performer by all accounts. One of the best. The RTX 4090 has changed that in a big way. It dominates at 1080p and 1440p and continues to do so at 4K, the only relevant resolution for an enthusiast-class card. User benchmark test results show an impressive 86% advantage for the 4090.
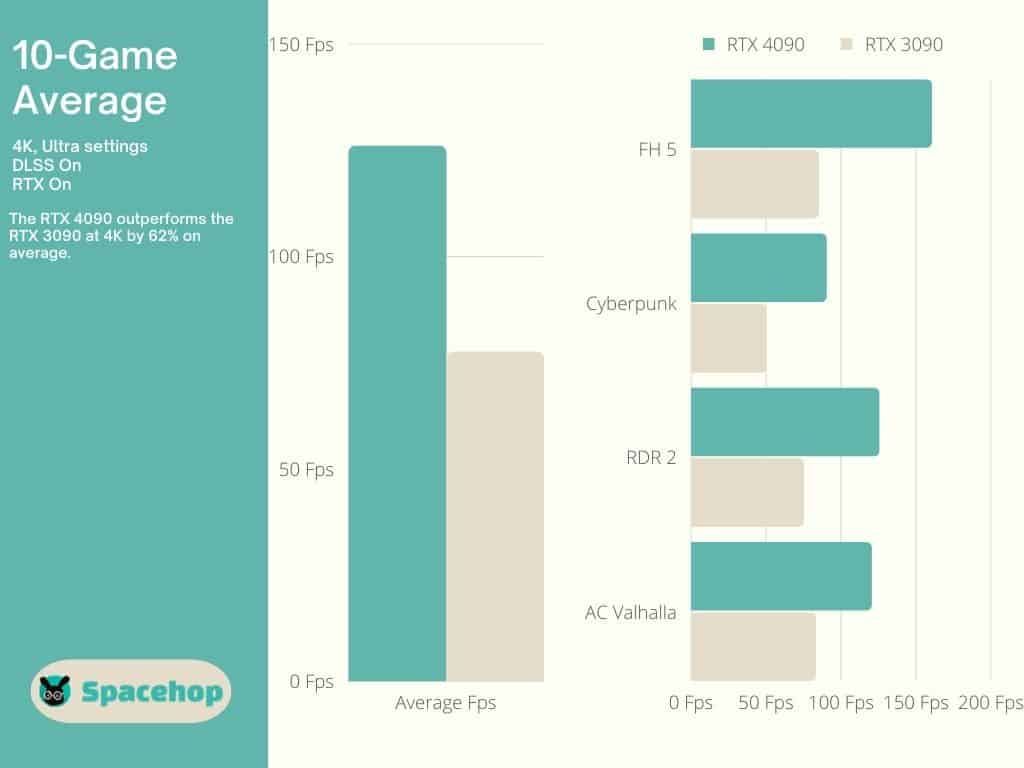
At 4K, the 4090 shows a 62% advantage in a ten-game performance test, including titles such as Cyberpunk, Red Dead Redemption 2, and Assasin’s Creed: Valhalla, all of which enjoy almost double the Fps they have on the RTX 3090. Both DLSS and RTX were on during testing. DLSS makes the most difference, as shown by Nvidia in this promotional video.
Winner: RTX 4090
Read Also: Difference between 4K and 1080p
Connectivity
Both the RTX 4090 and the 3090 support the same output connections; HDMI 2.1 and 1.4a DisplayPorts. You can find the supported resolutions below.
| RTX 4090 Output Type | Supported Resolution | RTX 3090 Output Type | Supported Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI 2.1 | 4K at 120Hz, 8K at 60Hz | HDMI 2.1 | 4K at 120Hz, 8K at 60Hz |
| DisplayPort 1.4a | 4K at 120Hz, 8K at 60Hz | DisplayPort 1.4a | 4K at 120Hz, 8K at 60Hz |
The RTX 40 series features 16-pin PSU connectors and they’re proving to be a bad call by Nvidia. Some users have reported their 16-pin catching fire, melting, and effectively destroying the card power port, leaving those users in quite a pickle.
Winner: Draw
TDP
TDP (Thermal Design Power) is a measurement of how much power a subsystem is allowed to draw from your PSU. It is also how much temperature that subsystem is allowed to produce (Thermal Design Point). The RTX 4090 requires an 850W PSU to draw its 450 W TDP from. It passes the 450 W mark when overclocked and draws just under 500 W in some cases.
The RTX 3090 is rated as a 350W card and requires a 750W PSU. Overclocked 3090 versions go slightly above these numbers but not by much. The maximum temperature for an RTX 3090 is set at 93℃ (199.4℉). Nvidia lowered the max temperature for the RTX 40 series to 90℃ (194℉).
The RTX 4090 FE hit 72℃ (161.6°F) during in-game testing, with fans running at around 40%. The RTX 3090 FE ran hotter, hitting 83℃ (181.4°F) during in-game testing. So, not only does the RTX 4090 deliver more performance, but it also does so at lower temperatures, even though it uses more power. Talk about efficiency.
Winner: Draw
RTX 4090 vs RTX 3090 – Pricing & Availability
You can’t expect low prices for either of these enthusiast-class cards. The RTX 4090 has an MSRP of $1,599, but I haven’t found a single deal remotely close to that price. The RTX 4090 Founders Edition is priced 86% above MSRP. The best performer available in the US, the MSI RTX 4090 SUPRIM LIQUID X, is priced 87% above MSRP.
The highest price I stumbled upon was for an ASUS ROG Strix variant, priced at a brazen-faced 130% above MSRP. The RTX 3090 went through this trend as well. It was launched with a $1,499 MSRP, but prices skyrocketed, fueled by crypto mining and scalpers looking to make a quick buck.
The No.3 variant on our best variant list, the ASUS ROG STRIX RTX GAMING OC is priced at 18-46% above MSRP. I found two variants now on sale; this EVGA Ultra Gaming variant is currently priced at 8% below MSRP, and this ZOTAC Gaming variant is priced at 13% below MSRP. These are great deals considering that a 3090 wasn’t available anywhere near MSRP for almost two years.
*Prices might be different at the time of reading.
Conclusion
There’s no doubt which card wins this 4090 vs 3090 comparison. The only problem is: where am I going to get three grand for a GPU?! That’s enough for a used car or an all-inclusive vacation. However, the same could be said of the RTX 3090 just six months ago. Prices will eventually drop for these cards.
If you’re looking for the absolute best in consumer-grade GPUs, the RTX 4090 has no competition and probably won’t, considering what I’ve seen at the RDNA 3 reveal. If you’re happy to have the next-to-best, the RTX 3090 is a great choice and will have you happily gaming for the foreseeable future.