A motherboard is one of the main computer components you look at when building a PC. For that reason, you need to pay attention when purchasing one. Motherboards have a lot of features, and you need to be aware of all of these details. In this article, we can help you with these details as we compare two great AMD chipsets — A520 vs B450.
A520 vs B450 – Quick Comparison
A520 and B450 belong to AMD AM4-based chipsets. There are three generations of these chipsets. The first number in the name defines the generation. So, the number 3 represents the first generation, 4 represents the second, and 5 represents the third generation. B450 was released in March 2018, and A520 was released in August 2020.

In general, AMD AM4 chipsets are compatible with AMD Ryzen 7th Gen A-Series, and AMD Athlon desktop processors. They usually come with DDR4 memory and USB ports with speeds of up to 10 Gb/s. Let’s see what features the chipsets in our A520 vs B450 comparison have to offer.
AMD A520

Pros:
- Supports up to 4733 MHz DDR4
- Lots of USB and SATA ports
- Variety of form factors
- Wi-Fi compatibility
Cons:
- Doesn’t support older CPU generations
- No SLI or Crossfire support
AMD B450

Pros:
- Vast range of supported CPUs
- Supports Crossfire technology
- Overclocking support
- More PCI-e lanes than A520
Cons:
- No SLI support
- Only two USB 3.2 Gen 2 ports
Socket and CPU Compatibility
Socket type supported
Do you think you can purchase any processor and pair it with any motherboard? This is far from the truth. They must be compatible to run properly, just like most computer components.
The connectivity between processors and motherboards comes down to the socket type. So, each of these components has to support the same socket-type connectivity. A520 and B450 support the same AM4 socket.
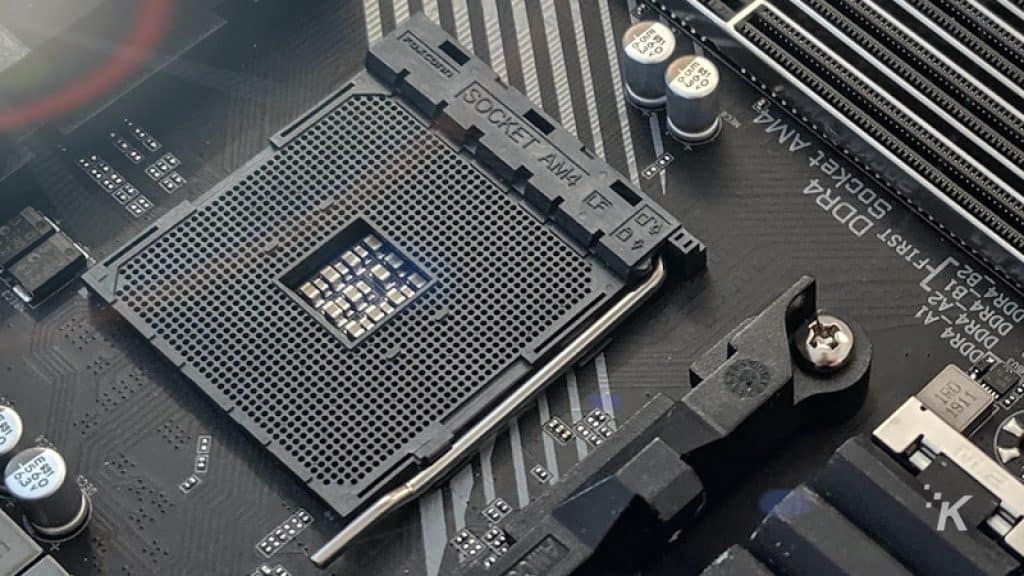

AM4 socket is compatible with CPUs built on Zen, Zen+, Zen 2, and Zen 3 microarchitectures. It has 1331 pins and supports DDR4 RAM. To conclude, you can connect the AM4 socket with AMD processors. For example, it would be impossible to connect an Intel Core processor with the AM4 socket motherboard.
CPU Support/Compatibility
As we mentioned above, these chipsets support AM4 sockets and AMD processors. However, when it comes to each individual chipset, you need to check out exactly which models they support. Let’s check it out in the table below.
| Processor | A520 | B450 |
|---|---|---|
| AMD Athlon with Radeon Graphics | No | Yes |
| AMD Ryzen 1000 | No | Yes |
| AMD Ryzen 2000 with Radeon Graphics | No | Yes |
| AMD Ryzen 2000 | No | Yes |
| AMD Ryzen 3000 with Radeon Graphics | No | Yes |
| AMD Ryzen 3000 | Yes | Yes |
| AMD Ryzen 4000 | Yes | Yes |
| AMD Ryzen 5000 | Yes | Yes |
As you can see, A520 supports only the newer generations of AMD processors. So, from Ryzen 3000 to 5000. On the other hand, B450 supports all of the AMD Ryzen generations, including Athlon processors with Radeon Graphics.
Form Factor
The form factor represents the physical state of the component. The motherboard form factor is directly related to computer cases. A motherboard’s form factor represents its size, shape, and design. So, each form factor is suitable for certain types of computer cases.
If you don’t know much about this subject, the first thing you should learn is what types of computer cases exist. Then you should get to know what types of motherboard form factors exist.
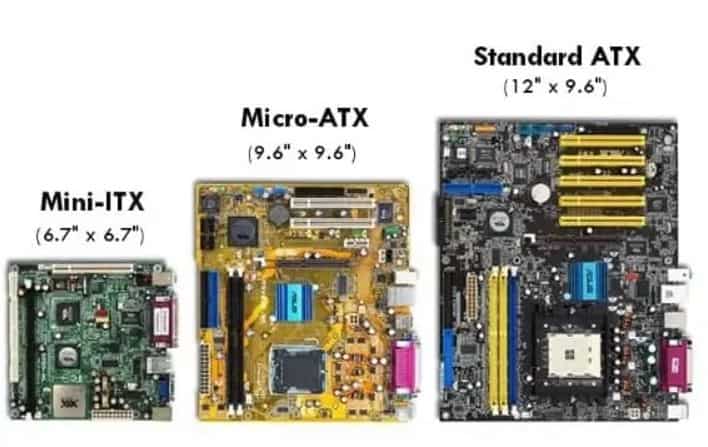
Basically, there are a couple of motherboard form factors:
- Mini ITX – 6.7 x 6.7 inches
- Micro ATX – 9.6 x 9.6 inches
- ATX – 12 x 9.6 inches
- EATX – 12 x 13 inches
Mini ITX is the smallest form factor, whereas EATX is the largest. Smaller form factors cost less, but they offer fewer PCI-e and RAM slots. The largest are more suitable for overclocking or multi-GPU configurations, and they offer more slots. However, they are more expensive, consume more power, and have an increased risk of overheating.
Even though most A520 and B450 motherboards are either ATX or Micro ATX, there are some that come in the Mini ITX form factor. Neither of these motherboards is available in the EATX form factor.
GPU Compatibility
SLI / Crossfire compatibility
With Nvidia’s SLI or AMD’s Crossfire technology, you can simultaneously use two or more graphics cards on the same motherboard. To enable this perk, you need to have multiple PCIe x16 slots on your motherboard.
You can connect up to four graphics cards, but you need free PCIe x16 slots. Additionally, the motherboard needs to support the technology.
SLI also requires that graphics cards are of the same model with the same memory. The manufacturer and clock speed are irrelevant. Crossfire requires only the same architecture.
However, the SLI setup is slightly more expensive than Crossfire. The reason is that a motherboard needs to have the “SLI certified” tag, which is not free. Therefore, that motherboard costs more since the manufacturer has to pay for such certification.
There are motherboards that support both technologies; some support just one of them, and some support neither.
In our A520 vs B450 comparison, you can’t really count on SLI technology since neither of the chipsets supports SLI. A520 doesn’t support Crossfire.
Only B450 motherboards, such as ASRock B450 Steel Legend support Crossfire technology.

Performance
Overclocking
If you want to enhance a computer’s performance without investing in new components, then overclocking is the thing for you. By overclocking, you can increase the frequency of computer components. You can increase it over the frequencies set by the manufacturer.
Most components, such as processors, memory, and graphics card, can all be overclocked. Usually, people overclock CPU and memory. By overclocking, you can get more out of your computer and improve its performance and gaming experience with no additional costs.
However, there are some downsides to this process. Overclocking can decrease the lifespan of your graphics card, processor, or any other component you want to overclock. Bear in mind that overclocking can cause overheating issues. Power consumption can increase, as well. Also, the warranty usually does not cover any damages caused by overclocking.
Unfortunately, A520 doesn’t support overclocking. So, if you wish to overclock components, B450 is a better choice.
Data transfer speed
Both of these chipsets support USB 3.2 Gen 2, with a speed of up to 10 Gb/s. However, they differ when it comes to the number of USB ports.
A520 has 13 USB ports in total, and five of them support USB 3.2 Gen 2. B450 has 14 USB ports in total, but only two of them support USB 3.2 Gen 2.
Memory speed / Compatibility
All motherboards with AM4 sockets come with DDR4 RAM support. The chipsets in our comparison have a maximum capacity of up to 128 GB. But they differ when it comes to speed.
B450 supports up to 3200 MHz, whereas A520 supports up to 4733 MHz.
Before investing in more RAM, you should know how much RAM your motherboard can handle.
Other Features
Wi-Fi compatibility
Having built-in Wi-Fi on your motherboard is a great addition. You can connect to Wi-Fi easily without needing a separate Wi-Fi card. Both A520 and B450 chipsets support Wi-Fi. However, we recommend that you check the specs for each individual motherboard and whether it supports Wi-Fi.
Connectivity options
As we mentioned earlier, these chipsets support USB 3.2 Gen 2, which means they support speeds of up to 10 Gb/s. But they have different numbers of USB ports. B450 has more USB ports in total. But A520 has more USB 3.2 Gen 2 ports.
| Connectivity Options | A520 | B450 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of USB ports | 13 | 14 |
| Transfer Speed | Up to 10 Gb/s | Up to 10 Gb/s |
| SATA 6.0 Gb/s Ports | 6 | 6 |
| PCI Express Lanes | 26 | 28 |
| PCI Express Generation | PCIe 3.0 | PCIe 3.0 |
The number of SATA ports is also the same. They also support the same PCI-e generation — PCI-e 3.0. However, they differ when it comes to the number of PCI-e lanes. A520 has 26 lanes, whereas B450 has two more.
BIOS
In order to run properly, some motherboards need a BIOS update. It is usually required if there is a need to support the new hardware, such as RAM or CPU. But the reasons could also be bug fixes or security patches.
Some A520 and B450 motherboards need a BIOS update, as well. Usually, older versions of CPUs require BIOS updates to run properly.
Future-proofing
It is difficult to determine which chipset is better in this segment because each chipset offers some future-proof features. A520 has fewer USB ports in total, but it has more USB 3.2 ports. It also supports faster RAM speeds.
B450, on the other hand, supports overclocking, Crossfire technology and has more PCIe lanes. So, it comes down to your priorities and which feature you prefer to use in the future.
However, we wouldn’t say that either of these chipsets is exactly future-proof. Neither of them supports DDR5 RAM. They also don’t support PCI-e 4.0, let alone PCI-e 5.0.
If you want better future-proof features such as DDR5 and PCI-e 5.0, check out other chipsets such as Intel B660 and Z690 or H670 and Z690.
Recommended A520 Motherboard
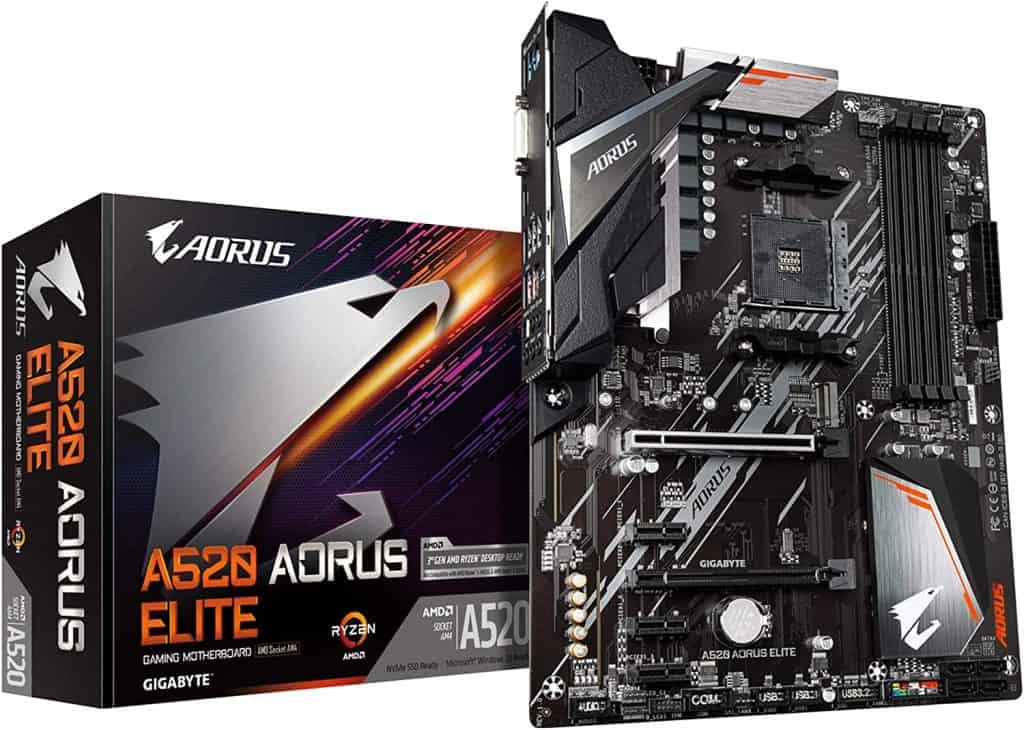
Gigabyte A520 AORUS ELITE
Gigabyte A520 AORUS ELITE supports up to 128 GB DDR4 RAM on four memory slots. The form factor of this motherboard is ATX. It has two PCIe x16 slots, one M.2 connector, and four SATA 6 Gb/s ports.

Recommended B540 Motherboard
Asus ROG STRIX B450-F GAMING II
Asus ROG STRIX B450-F GAMING II supports up to 128 GB DDR4 memory via 4 x DIMM channels. It has three PCIe x16 slots (two support PCIe 3.0, and one supports PCIe 2.0).
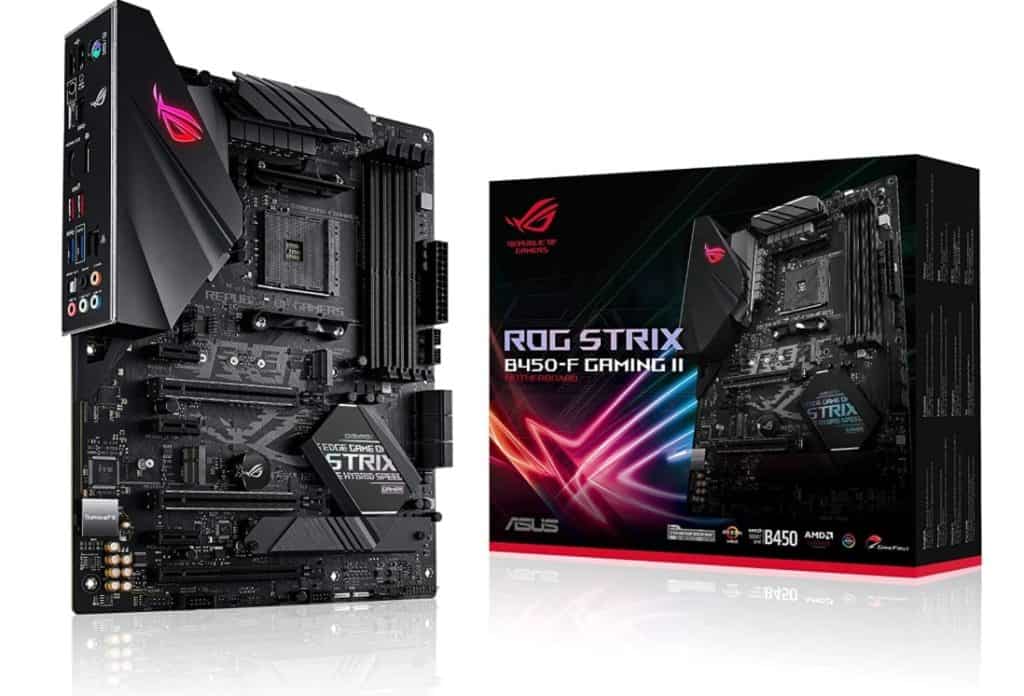

On the front, it has two USB 3.2 Gen 2 ports, and on the rear, it has two USB 3.2 Gen 1 ports. It has six SATA ports and two M.2 slots. Its form factor is ATX, and it is Crossfire capable.
Conclusion
To conclude this A520 vs B450 comparison, let’s see what their best features are.
A520 chipset supports up to five USB 3.2 Gen 2 ports and has many SATA ports. It supports high RAM speeds of up to 4733 MHz. You can also choose from a variety of form factors. As such, it is perfect for demanding home or office users.
B450 is compatible with a huge variety of processors and has plenty of USB ports and PCIe lanes. It supports multi-GPU Crossfire technology and overclocking. So, it is a great choice for power users who appreciate overclocking features.