Looking for a new motherboard? Want a motherboard of a newer generation but not sure which one to choose? You can opt for a motherboard with a chipset from the Intel 600 series of chipsets. They support the newest generation of Intel Core processors and have lots of great features. In this article, we compare B660 vs Z690 Intel chipsets.
B660 vs Z690 – General Overview
Chipsets in our comparison belong to the Intel® 600 Series of chipsets. Since they are part of the same series, they are very similar in terms of the technologies they support. However, they differ in some aspects.

The main differences come down to the number of ports, PCI-e lanes, and CPU overclocking. But let’s see a more detailed comparison of the two.
Intel B660

Pros:
- Supports the 13th Gen Intel Core processors
- PCI-e 5.0 support
- Supports DDR5
- Wi-Fi support
Cons:
- Doesn’t support SLI technology
- No CPU overclocking support
Intel Z690

Pros:
- Up to 28 PCI-e lanes
- Lots of USB and SATA ports
- Supports both SLI and Crossfire
- EATX form factor
Cons:
- Some motherboards support only up to 64 GB RAM
- Can be pricey
Socket and CPU Compatibility
Socket type supported
In order to connect a processor to your motherboard, it needs to have a matching socket type. The 600 Series of Intel chipsets come with the LGA 1700 socket. It is a successor of the LGA 1200 socket.
When compared to its successor, the LGA 1700 has 500 more pins, an improved power delivery, and is bigger in size. Therefore, if your CPU is compatible with LGA 1700, you can’t combine it with a motherboard that has an LGA 1200 socket type.
That said, the Intel 600 series of chipsets, including B660 and Z690, support 12th and 13th Generation Intel Desktop Processors.
CPU support/compatibility
As shown in the table below, both of these chipsets support Intel Core processors, Pentium Gold processors, and Celeron G Series processors.
| B660 Compatible Processors | Z690 Compatible Processors |
|---|---|
| 13th Generation Intel Core i9 Processors | 13th Generation Intel Core i9 Processors |
| 12th Generation Intel Core i9 Processors | 12th Generation Intel Core i9 Processors |
| 13th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors | 13th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors |
| 12th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors | 12th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors |
| 13th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors | 13th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors |
| 12th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors | 12th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors |
| 12th Generation Intel Core i3 Processors | 12th Generation Intel Core i3 Processors |
| Intel Pentium Gold Processor Series | Intel Pentium Gold Processor Series |
| Intel Celeron Processor G Series | Intel Celeron Processor G Series |
What is great about these chipsets is that they support the latest 13th Generation Intel Core processors, including their fastest processor — Intel Core i9-13900K.
If you are getting a new computer or simply replacing the CPU on your existing one, make sure to read our article comparing different Intel Core processors. Especially pay attention to the most recent Intel Core i7 vs i9 processors.
Form Factor
If you think that all motherboards are the same size, you are mistaken. They differ in size, design, and even shape. We recommend learning more about them before purchasing a motherboard. You need to have a suitable PC case and power supply, depending on the form factor.
The most common form factors of motherboards are ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini ITX. Mini ITX is the smallest, while ATX is the largest. They differ not only in size but also in the number of slots. Mini ITX has only one PCI-e and one RAM slot. Micro ATX has four of each, and ATX has up to seven PCI-e slots and up to four RAM slots.
Being the largest, ATX motherboards take up more space, require more power, and can be pricey. While Micro ATX and Mini ITX take less space, they have fewer slots and are not suitable for overclocking or running multiple GPUs parallelly.
Both B660 and Z690 motherboards come in a variety of form factors. So, you can find ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini ITX versions of B660 motherboards and Z690 motherboards.
However, the only difference is that Z690 motherboards also come with an EATX form factor. For example, MSI MEG Z690 ACE or Asus ROG MAXIMUS Z690 EXTREME.

An EATX (extended ATX) motherboard is even larger than an ATX motherboard. Accordingly, they come with more PCI-e and RAM slots.
GPU Compatibility
SLI / Crossfire compatibility
If you were wondering, it is possible to use multiple graphics cards simultaneously on the same motherboard. But motherboards have to be suitable for such use. This is achievable via Nvidia’s SLI or AMD’s Crossfire technology.
Each technology allows you to connect up to four graphics cards to one motherboard. SLI, however, requires that each of these is the same model with the same memory. It allows different clock speeds and manufacturers.
Crossfire, on the other hand, requires only the same architecture. So, you can connect graphics cards from different manufacturers with different memory sizes and clock speeds.
The main advantage of these technologies is that you will enhance your graphics performance. However, the downside includes overheating issues and power consumption.
If you use multiple graphics cards, you will need more power. Also, you may encounter overheating, so you should have a good cooling system in place.
In our B660 vs Z690 battle, only Z690 supports both technologies. Unfortunately, B660 doesn’t support SLI technology, but it does support Crossfire. For example, MSI MAG B660 TOMAHAWK WIFI supports Crossfire.

Z690 motherboards are more versatile. Some support both technologies, and some only support one of them. For example, MSI MEG Z690 ACE supports both SLI and Crossfire.

Performance
Overclocking
Overclocking, or pushing the component’s speed over its set limits, is either supported by a chipset or not. Generally speaking, overclocking is possible for almost any computer component.
But the most frequently overclocked components are the processor and memory. There is no difference between B660 and Z690 when it comes to memory overclocking since they both support it.
The good news is that both of these chipsets support Intel’s XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) feature. This feature allows you to overclock DDR4 or DDR5 memory. You can turn this feature on from the BIOS. That way, you can use the maximum potential of your memory.
However, one of the main differences between these two chipsets is support for CPU overclocking. B660 doesn’t allow CPU overclocking, whereas Z690 does. For that reason, the Z690 is a better choice if you constantly try to squeeze better performance out of your computer.
Data transfer speed
Data transfer speed comes down to the speed of the USB port. There are different versions of USB ports. They range from USB 2.0 up to 3.2 Gen 2×2. All of these offer different transfer speeds. The base USB 2.0 has a speed of up to 480 Mb/s.
The USB 3.2 versions offer much higher speeds. So, USB 3.2 Gen 1 has a speed of up to 5 Gb/s, and Gen 2×1 has a speed of up to 10 Gb/s. USB Gen 2×2 is the fastest and offers a speed of up to 20 Gb/s.
However, keep in mind that those are theoretical speeds. In reality, you can expect somewhat lower speeds, which you can see in the picture below.
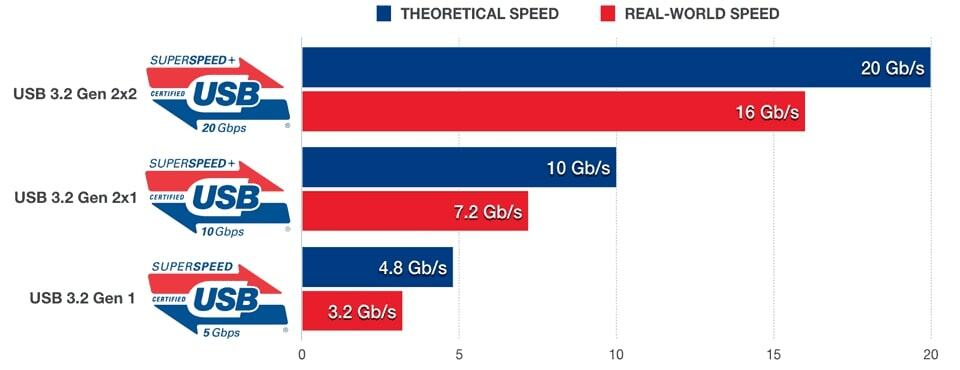
When we compare B660 and Z690, we can see that the Z690 has a higher number of USB ports. More importantly, they both support the fastest generation (3.2 Gen 2×2), meaning they can both offer a speed of up to 20 Gb/s.
The only difference is that B660 offers only two of these ports, whereas Z690 offers two more, for a total of four.
| Chipset | 2.0 | 3.2 Gen 1×1 | 3.2 Gen 2×1 | 3.2 Gen 2×2 | Total number of USB ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B660 | 12 ports | Up to 6 ports | Up to 4 ports | Up to 2 ports | 12 |
| Z690 | 14 ports | Up to 10 ports | Up to 10 ports | Up to 4 ports | 14 |
Memory speed / Compatibility
B660 and Z690 support both DDR4 and DDR5 memory. As shown in the table below, they also support the same speeds. So, each of them supports a speed of up to 3200 MT/s when it comes to DDR4 and up to 4800 MT/s when it comes to DDR5 memory.
| Memory Type | B660 | Z690 |
|---|---|---|
| DDR4 | Up to 3200 MT/s | Up to 3200 MT/s |
| DDR5 | Up to 4800 MT/s | Up to 4800 MT/s |
When it comes to capacity, most B660 motherboards support up to 128 GB of memory and four memory slots. However, there is a significant number of them (third-party versions) that support only up to 64 GB and two memory slots. The Z690 also supports up to 128 GB and four memory slots or 64 GB and two memory slots.
For example, Asus ROG STRIX B660-I GAMING WIFI supports up to 64 GB and two memory slots. This is mainly because its form factor is Mini ITX, and accordingly, it has fewer memory slots.
Other Features
Wi-Fi compatibility
B660 has an integrated Wi-Fi 6E AX211 or Wi-Fi 6E AX210 solution, whereas Z690 has an integrated Wi-Fi 6E AX211 or Wi-Fi 6E AX210 solution. Therefore, both of these support WiFi 6E.
WiFi 6E is basically just an extended version of WiFi 6. What this means is that WiFi 6E has the same features as WiFi 6, but it extends access to the 6 GHz band.
However, not all motherboards with these chipsets come with an integrated Wi-Fi solution. For example, MSI PRO Z690-A doesn’t have Wi-Fi support. Therefore, you need to check whether each individual motherboard is Wi-Fi compatible before you make a purchase.
Connectivity options
Both of these chipsets support the fastest USB speeds of up to 20 Gb/s. However, the Z690 has more USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 ports and more ports overall. It also has a significantly higher number of SATA 6.0 Gb/s ports. Z690 has eight SATA ports, while B660 has only four.
| Connectivity Options | B660 | Z690 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of USB ports | 12 | 14 |
| Transfer Speed | Up to 20 Gb/s | Up to 20 Gb/s |
| SATA 6.0 Gb/s Ports | 4 | 8 |
| PCI Express Lanes | 14 | 28 |
| PCI Express PortConfigurations | 1×16+1×4 | 1×16+1×4 or 2×8+1×4 |
| Ethernet | Yes | Yes |
| DMI lanes | 4 | 8 |
The overall number of PCI Express lanes also differs. The Z690 has up to 28 PCI Express lanes, whereas B660 has only 14. Let’s look closer at the structure of these lanes.
| PCI-e | B660 | Z690 |
|---|---|---|
| PCI-e 5.0 lanes | 1×16 | 1×16 or 2×8 |
| PCI-e 4.0 lanes | 6 | 12 |
| PCI-e 3.0 lanes | 8 | 16 |
As we can see, the Z690 has a higher number of PCI-e lanes in general, so it is a better choice in this segment.
The B660 and Z690 both support PCI-E 4.0 for SSDs, but they have a different number of M.2 slots. The Z690 has more available PCI-e lanes; therefore, it has more m.2 slots.
For example, let’s compare two ASUS ROG STRIX motherboards. The B660-I GAMING WIFI version has 2 M.2 slots, while the Z690-E GAMING WIFI version has three M.2 slots.
BIOS
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is software that enables the communication between your operating system and the computer’s hardware. Sometimes, a BIOS update is required if there is a need for security patches, bug fixes, or support for new hardware.
When you install a new RAM or CPU, you might need to update the BIOS so that the motherboard can identify them.
Regarding the Intel 600 series, including B660 and Z690, there is a need for a BIOS update. Intel recommends that you update BIOS if you want to boot the 13th Generation of Intel Core processors.
Future proofing
The true representation of future-proofing is PCI-e 5.0. The reason is that PCI-e 4.0 offers more than enough for today’s graphics cards. It is also expected that it will be enough for the next generation of GPUs.
Therefore, PCI-e 5.0 is a technology of the future. Luckily, the Intel 600 series and B660 and Z690 chipsets both support PCI-e 5.0. So, if you are a fan of future-proofing, either one of these chipsets is a good choice when it comes to PCI-e.
However, you should take into consideration other factors, as well. The Z690 has overall more PCI-e 4.0 and 3.0 lanes. It also has more USB ports, SATA ports, and DMI lanes. And last but not least, it supports CPU overclocking.
Therefore, in terms of future-proofing, Z690 is a better choice. But keep in mind that these motherboards are pretty expensive. So, they are future-proof, but you need to be prepared to invest a little bit more money in them.
If you want to know how B660 compares with other chipsets in the 600 series, read our articles on how it compares to the H610 or H670. Also, check out our Z590 vs Z690 and H670 vs Z690 comparisons!
Recommended B660 Motherboard
MSI MAG B660M MORTAR WIFI
The MSI MAG B660M MORTAR WIFI is a B660 motherboard with a Micro ATX form factor. It supports up to 128 GB of DDR4 memory on four memory slots.
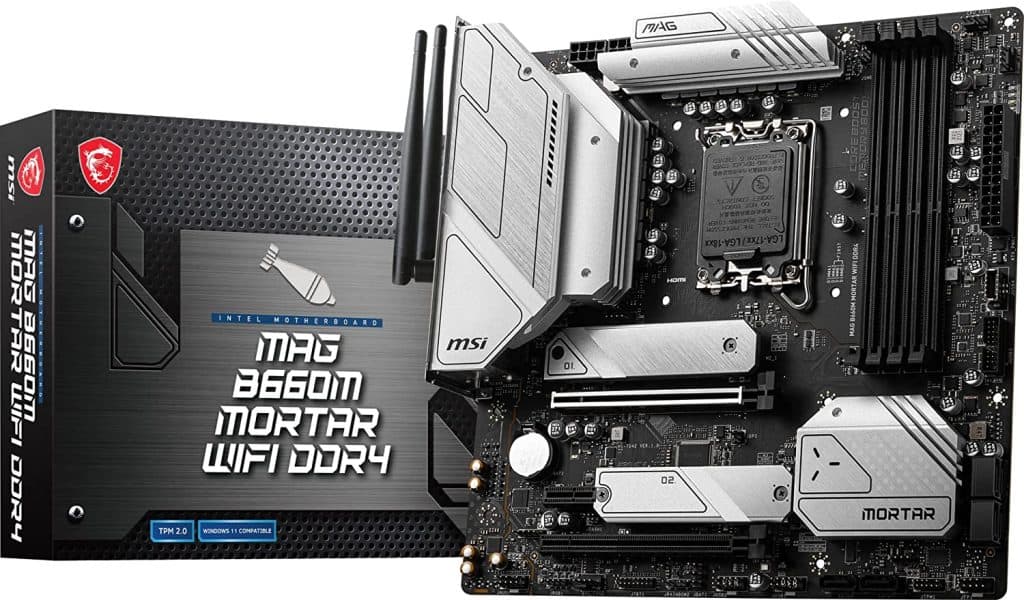

It has two PCI-e x16 slots, two M.2 slots, and six SATA III slots. It has a USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 Type-C port with a speed of up to 20Gb/s. It also supports Wi-Fi 6 and Crossfire technology.
Recommended Z690 Motherboard
ASUS ROG Strix Z690-E Gaming WiFi
The ASUS ROG Strix Z690-E Gaming WiFi supports up to 128 GB of DDR5 RAM on four memory slots. It has three PCI-e x16 slots, five M.2 slots, and six SATA 6.0 Gb/s slots. Besides DDR5 memory, you can count on PCI-e 5.0, as well.
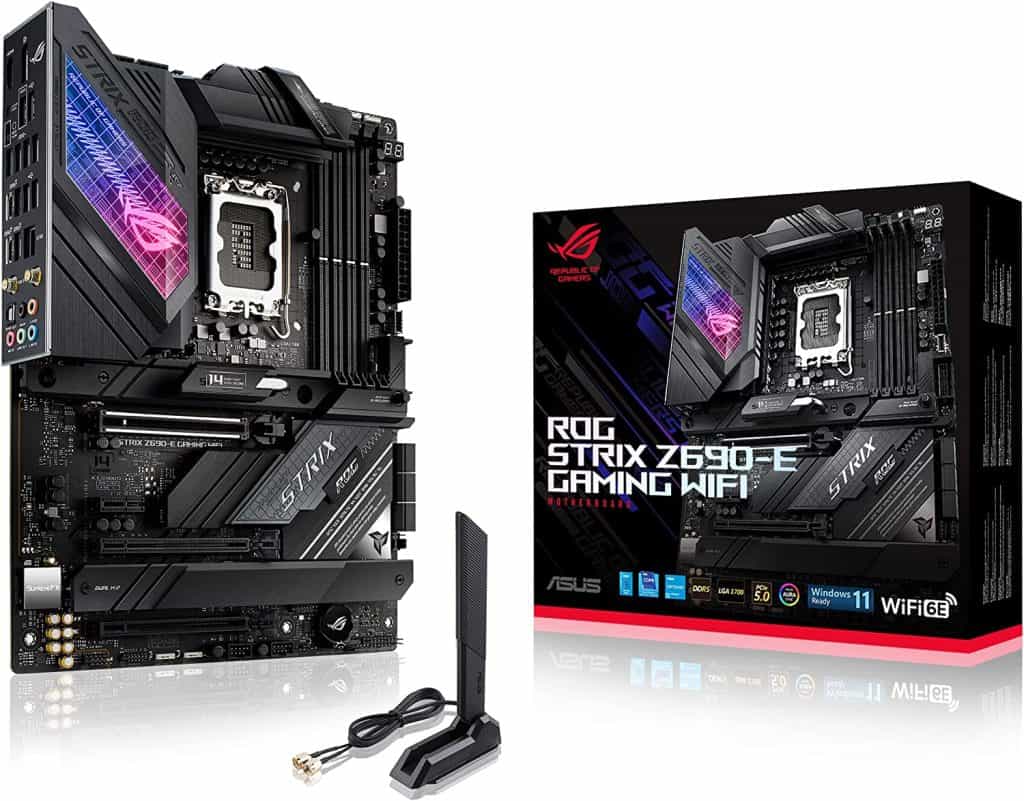

It comes with a USB 3.2 Gen 2×2, and overall, it has 10 USB ports on the rear and seven on the front. It supports WiFi 6E or 2.4/5/6 GHz frequency band. It has many AI features, such as two-way noise cancellation, overclocking, cooling, and networking.
Conclusion
To conclude this B660 vs Z690 comparison, let’s recap their best features. Both of these chipsets support the 12th generation and the latest 13th generation of Intel Core processors.
B660 comes in a variety of form factors and supports lots of great features like USB 3.2 Gen 2×2, Crossfire, and memory overclocking. It is compatible with both DDR4 and DDR5 RAM, and it supports Wi-Fi connections.
In addition to ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini ITX form factor, Z690 also supports the EATX form factor, which is a great choice for overclocking and running multiple GPUs. Besides that, it has up to 28 PCI-e lanes and plenty of USB and SATA ports. When you add the support for PCI-e 5.0 and DDR5, this is a great choice if you are a fan of future-proofing.