When it comes to processors, it can be easy to think that the flashiest option, which costs the most and has the most cores, is going to be the “best.”
Not so with the AMD Ryzen 5 and AMD Ryzen 7 processors. Generally speaking, the Ryzen 7 might cost more than the Ryzen 5; the latter doesn’t disappoint in almost any category where the two are compared.
Let’s compare the Ryzen 5 vs Ryzen 7 and see how they stack up.
Ryzen 5 vs Ryzen 7
For most of recent tech history, AMD has been a few steps behind Intel, and both the price and performance of their processors showed it. But in 2016, AMD pulled out the big guns, revealing its new Zen architecture, putting it back on the board, directly competing with Intel on both price and performance.
The Ryzen processors are credited with that success, credit which is certainly warranted when you consider that AMD regularly tops charts when compared to Intel processors and almost always takes home the gold when it comes to a budget category.
And that really is what makes AMD special. Sure, they put resources into making ridiculous products that have ridiculous performance. Still, they know that what normal people need and want is a decent processor for a reasonable price, and that’s what they provide.
That is to say that the Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 are where they really shine.
Ryzen 5
- Pros
- Less power consumption
- Less heat output
- Cons
- Dedicated GPU is generally required
- Less cores/threads
- Lower clock speed
- Generally weaker performance
- Can’t run faster RAM
Ryzen 7
- Pros
- More cores/threads
- Higher clock speed
- Can run faster RAM
- Generally better performance
- Cons
- A dedicated GPU is generally required
- More power consumption
- More heat output
Comparing Specs
Cores
The cores in a processor give you a pretty good idea of how many things that processor can do at one time—generally, the more cores, the better the performance.
Ryzen 5 processors typically come in either 4 core or 6 core models, with most modern ones having 6. This many cores is not just great for general purpose stuff, like running a web browser or playing light games, but it even inches into a higher-performance category, managing multiple things at once with ease.
Ryzen 7 goes even a little further up, usually having 8 cores. This is really the official start to high-tier processors, and 8 cores mean that you can have several multi-core programs (like video editing or complex design programs) going at one time.
Threads
Threads break down the process that a core is working on into even smaller bits, managing them separately. The more threads in a core, the more pieces the core can break a process down into, and the better it can get it done. Again, the more, the better.
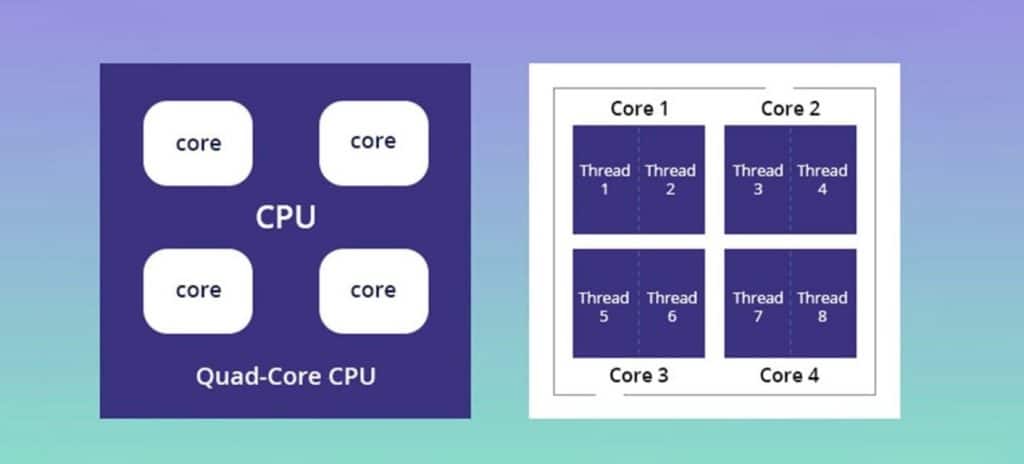
Generally, relevant versions of both Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 processors have two threads per core, resulting in either 8 or 12 threads on a Ryzen 5 and 16 on a Ryzen 7.
All of this means that the individual cores will be able to do more things simultaneously, so if your goal is to run several applications at once, more threads is probably a good goal. If you only do one thing at a time, though, saving some money and sticking with fewer threads isn’t a bad plan.
Clock Speed
Both processors usually do a great job in their clock speeds, which is essentially how fast data can get pushed through each core and thread. However, this is also partially limited by how well the processor is cooled, so keep in mind that you might not get perfect speeds without proper cooling solutions.
The Ryzen 5 line generally has regular base speeds of around 3.6GHz, with boost speeds up to 4.2GHz on some processors. This is a very comfortable spot for almost anything you could want to do, from gaming to watching YouTube, from editing word documents to editing videos.
The Ryzen 7 processors do a little bit better, with their base speeds around 3.9GHz, and their top speeds as high as 4.5GHz. These are great numbers, especially when you consider the number of cores being used at that speed, but it’s important to make sure the processor stays cooled, or it won’t last long there.
Cache
A processor’s cache stores data it uses frequently, and the more cache there is, the more smoothly things tend to go in the long run. More cache means your processor has to spend less time going and looking for the data it needs.
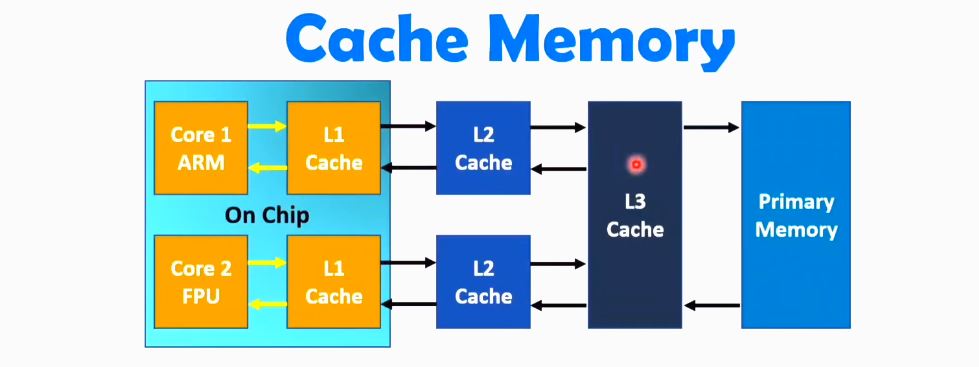
Both the Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 have 32MB of cache, which in fairness, can make it a little difficult to compare. That said, rest easy knowing that the 32MB of cache in these Ryzen processors is the most you can find at this price point, making it money well spent if that’s what you choose.
Socket
Socket types don’t relate hardly at all to performance, but they do relate to whatever motherboard you might be getting.
The good news is, if you’re looking for a motherboard, your job is pretty easy between these processors. This is because both use the same socket, called AM4.
Integrated Graphics
Some Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 processors run AMD’s Radeon RX Vega 11 integrated graphics, meaning that a graphics card isn’t necessarily required to boot and run a system with these processors.
Most Ryzen processors, though, come without integrated graphics in them, meaning you need a dedicated graphics card for the system to boot anything to your monitor. Of course, the expectation here is that any system with these processors is within a price point that can afford a discrete GPU, but if you aren’t planning on that, make sure whatever you choose has integrated graphics.
That said, don’t expect high graphics performance without a GPU anyways. Integrated graphics will let you browse the web, maybe even play a couple of very light games at a low frame rate, but if you want heavy-duty graphics performance, you need to install a discrete graphics card.
TDP
TDP stands for “Thermal Design Power,” though in all technicality, it is a measurement of how much heat a processor can handle. Thus, it really represents how much power a processor consumes during its usage.
The Ryzen 5 line tends to fall around where the normal TDP for this kind of processor is, around 65W at default. With this, you don’t have to worry too much about cooling or excessive power consumption.
The Ryzen 7 is a little bit different. Different specific processors behave differently, but TDP for Ryzen 7 ranges from 65W (the same as the Ryzen 5) all the way up to 105W at default. With these, it’s a little more important to make sure you have a power supply that can handle the power draw and a cooling solution that makes sure it doesn’t overheat.
Other Features
Both Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 processors take advantage of AMD’s symmetric CCX layout, which means that the cores are distributed evenly through the processor. This means that you basically get a little more cache than you would with an Intel processor at the cost of a tiny bit more latency.
Both lines have dual-channel capability when it comes to memory, but the difference between them is that Ryzen 7 can handle higher-speed memory (up to 3200MHz) than the Ryzen 5 can (Only 2933MHz).
All Ryzen processors come unlocked, so for those enthusiasts out there looking to get some extra performance out of their processor, go crazy. Just make sure you manage to cool it properly, or else you can damage the processor when trying to overclock it.
Of course, like any processor, some of the performance of both the Ryzen 5 and the Ryzen 7 is based on how well they’re cooled. The stock cooler that comes with them will usually work fine, but if you really want to push it to the max, it might be worth investing in an aftermarket fan cooler or even a water cooling solution.
Example Comparison Ryzen 5 3600X vs Ryzen 7 3800X
To get a practical idea of the differences and similarities between the AMD Ryzen 5 and AMD Ryzen 7 processors, let’s look at some specific models. Here, we can look at the Ryzen 5 3600X and the Ryzen 7 3800X.
| Ryzen 5 3600X | Ryzen 7 3800X | |
|---|---|---|
| # of cores | 6 | 8 |
| # of threads | 12 | 16 |
| Base clock speed | 3.6GHz | 3.9GHz |
| Max clock speed | 4.2GHz | 4.5GHz |
| TDP | 65W | 105W |
| Total cache | 32MB | 32MB |
| Socket | AM4 | AM4 |
| Integrated Graphics | None | None |
| Unlocked? | Yes | Yes |
| Price | Check Price on Amazon | Check Price on Amazon |
Looking at core and thread count, the Ryzen 7 3800X clearly comes out on top, but not by too much. The two extra cores there make a difference for high-capacity users, no doubt, but for most ‘normal’ users, meaning people who only do one or two big tasks at a time, the six cores and 12 threads on the Ryzen 5 3600X would work totally fine.
When it comes to clock speed, the difference is a little more clear-cut. The extra speed in the Ryzen 7 means that even on single-core applications, the processor will work fast enough to keep up. However, the difference between the base speed and the max speed isn’t any different on the Ryzen 5, so the Ryzen 7 takes the gold in this category, hands down.
With the same amount of cache (which is still quite a bit when you compare it to an Intel processor), they both do well and deserve credit.
Looking at TDP, though, reveals the weakness of the Ryzen 7, which is that it is a power-hungry machine. All that power means a lot of heat would be generated, and even a stock cooler wouldn’t realistically keep up. So without a more sophisticated cooling solution, the win here goes to the Ryzen 5 3600X.
Overall, the difference here is what kind of computer you’re looking to have. If you’re willing to put a little extra money into your computer to boost the graphics with a GPU, as well as to add some other cooling solutions to the mix, then the Ryzen 7 3800X is for you.
But if you’re a ‘normal’ user, and you want a decent processor without too much extra maintenance required, the Ryzen 5 3600X might be the better option. Plus, it comes with the added bonus of being cheaper.
Conclusion
When it comes to Ryzen 5 vs Ryzen 7, both lines of processors are meant to perform on heavier workloads than the average office job might deal with. This can mean more complex programs, like video or photo editing or gaming, but overall, both can handle sophisticated software well.
The Ryzen 5 is a great choice for people who need a no-nonsense processor. Versions with integrated graphics mean that it doesn’t always require extra investment in a discrete GPU. It has more than enough capacity to handle anything the average user could want to do with it.
The Ryzen 7, however, is more for enthusiasts or high-level users. It performs at a high level, but it comes not only at the extra cost for the chip but the extra cost for a GPU (for certain models) and better cooling. But, in return, you get a powerful processor that shows up for almost any job you need it for.

