When AMD first rolled out the Ryzen series, the world saw a significant leap in CPU technology. And two such CPUs, the Ryzen 7 2700 and Ryzen 5 3600 stand very close to each other although intended for different purposes.
Both have similar clock speeds, support fast DDR4 RAM, and let’s not forget about the proprietary overclocking technology. But some differences cannot be dismissed. So, we made a comparison to find out which one is better for you.
Ryzen 7 2700 vs Ryzen 5 3600
AMD is one of the largest manufacturers of microprocessors for general use and gaming. And over the years, it has developed a wide range of processors, including the Ryzen 7 2700 and the Ryzen 5 3600.
The Ryzen 7 2700 is for high-performance users. It’s the perfect choice for gamers and those who have to handle large projects on their desktops. While that’s impressive, the Ryzen 5 3600 is no bystander either. Designed for the mainstream user who doesn’t have significant power demands, it boasts higher speeds with more cores. The result is a processor that isn’t too far from the higher-end Ryzen 7 CPUs.
| Features | AMD Ryzen 7 2700 | AMD Ryzen 5 3600 |
|---|---|---|
| Cores | 8 | 6 |
| Threads | 16 | 12 |
| Clock Speed | 3.2 GHz (Base), 4.1 GHz (Max) | 3.6 GHz (Base), 4.2 GHz (Max) |
| Cache Sizes (L1, L2, L3) | 768KB, 4MB, 16 MB | 384 KB, 3MB, 32MB |
| Socket | AM4 | AM4 |
| Integrated Graphics | No | No |
| RAM Compatibility | DDR4 (2933 MHz) | DDR4 (3200 MHz) |
| TDP | 65W | 65W |
| Microarchitecture | Zen+ | Zen2 |
| Intended Use | High-Performance users | Mainstream users |
| Price | Check Price on Amazon | Check Price on Amazon |
AMD Ryzen 7 2700

Pros
- More cores
- Better overclocking
- Made for high-performance use
- Great for gaming
Cons
- Slower base speed
- Slower RAM speed
AMD Ryzen 5 3600

Pros
- Faster RAM speed
- Faster base clock
- More shared L3 cache
- Made for mainstream users
Cons
- Less individual cache
- Lesser number of cores
Key Specifications
Cores
You may have heard of the terms “dual-core” and “octa-core,” but what do those terms mean? Cores are the physical divisions inside the processor. Each core is an independent processing unit with its memory and controlling circuit. The more the cores, the higher the processing power of the processor.
In that regard, the Ryzen 7 2700 features 8 cores. The Ryzen 5 3600 is a Hexa-core processor, meaning it has 6 cores. The Ryzen 7 2700 has an optimal number of cores. It’s similar to what other processors in this family offer. Plus, considering it’s meant for high-performance users, the number of cores it offers is perfect for demanding gamers and creators.
Ryzen 5 3600 is for the mainstream user. However, most processors made for this purpose only offer 4 cores. So, the addition of 2 more cores is an improvement. This enhances the performance of the processor. And it optimizes it for higher-end tasks such as simultaneously running several high-end video and image editing applications.
Winner: Ryzen 7 2700
Clock Speed
When talking about processing power, one major factor is clock speed. Every processor has an internal clock. It determines how fast the processor will run. The faster the clock, the more operations the processor can perform in a single second.
Ryzen processors have two clock speeds, the Base Clock and the Max Boost Clock. The Base Clock is the speed at which the processor runs typically. And the Max Boost Clock is the max speed attainable by a single core.
Being a higher-end processor, you would expect the AMD Ryzen 7 2700 to be faster. However, that’s not the case. Instead, the AMD Ryzen 5 3600 is the faster processor. More specifically, the Ryzen 5 3600 is 3.6 GHz while the Ryzen 7 2700 is 3.2 GHz.
However, when it comes to Max Boost Clock speed, both of their speeds come pretty close. The Ryzen 7 2700 has a Max Boost Clock frequency of 4.1 GHz, and that of the Ryzen 5 3600 is 4.2 GHz. This means the Ryzen 5 will outperform the Ryzen 7 on an average day. But when push comes to shove, they both can reach incredible speeds and adapt to the workload.
Winner: Ryzen 5 3600
Threads
The threads of a core are the virtual divisions in the core that help further divide the work. Cores can have up to 2 threads. The more threads in a single core, the more tasks it can handle simultaneously.
The AMD Ryzen 7 2700 uses a technique called “hyperthreading.” In the most basic sense, it uses 2 threads per core, for a total of 16 threads for 8 cores.
And the same technique is used in the AMD Ryzen 5 3600. It features 12 threads, with 2 threads on each of the 6 cores. Considering it’s a powerful mainstream processor, hyperthreading is a definite plus. In addition, Hyperthreading allows for better multitasking, enabling the processor to handle a heavier workload.
But since the Ryzen 7 2700 has more threads, it’s the clear winner here.
Winner: Ryzen 7 2700
Socket
When you’re mounting a processor onto the motherboard, you’ll most likely find a dedicated socket. First, you must make sure the socket on your motherboard is compatible with the processor you want to install. If your motherboard doesn’t have a socket, it’s a good idea to get one compatible with your processor. Sockets make it easy to remove, replace, and re-mount processors.

Luckily, AMD provides a lot of flexibility. Both the AMD Ryzen 5 3600 and the Ryzen 7 2700 use the AM4 socket. The AM4 socket is widely used in many Ryzen processors. This means you can experiment with both the processors on the same motherboard.
Cache
Every CPU requires memory. When your CPU needs to store information temporarily, it stores the data in RAM. But since RAM is not inside the CPU, internal memory is required. This is the cache. It’s usually smaller than RAM but faster and can be accessed almost immediately.
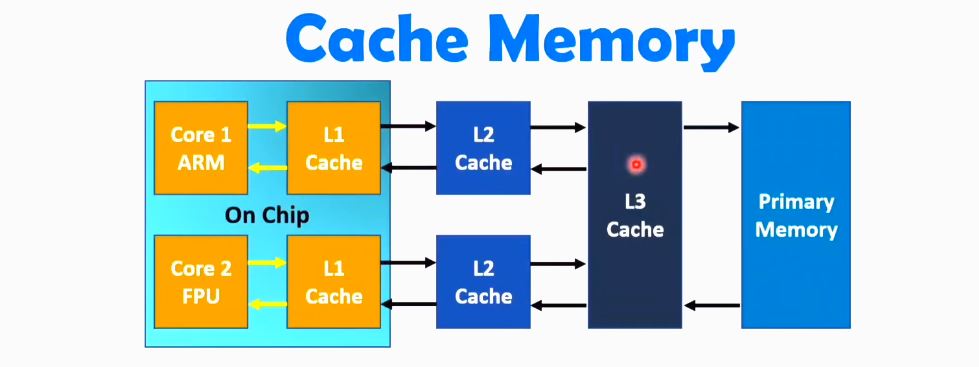
In modern processors, the cache can have up to three “levels.” The first two levels are unique to each core, while the third level, called the L3 level, is shared across cores.
And that’s the same design both the AMD Ryzen 7 2700 and Ryzen 5 3600 follow. They have three levels of cache, with the first two levels being unique to each core and the third level being shared.
On the Ryzen 7, the L1 and L2 caches are 768KB and 4MB, respectively. And the L3 cache has a total capacity of 16 MB. On the other hand, the Ryzen 5 has L1, L2, and L3 cache capacities of 384KB, 3MB, and 32MB. Hence, the Ryzen 5 3600 has more shared cache but less cache unique to each core.
Winner: Tie
Integrated Graphics
Some CPUs have integrated graphics, which eliminates the need for a discrete GPU. However, while the AMD Ryzen 5 and 7 families are available with integrated graphics, the Ryzen 7 2700 and the Ryzen 5 3600 are not. These processors come without any integrated graphics.
On the plus side, this means you don’t have to pay extra for integrated graphics if you already have a discrete GPU. If not, however, then either buy one or choose a different Ryzen CPU.
Ram Compatibility
RAM is the temporary memory CPU needs to store information before, during, and after processing. More RAM can run memory-hungry applications on your device. Aside from the capacity, the type of RAM is also a crucial buying factor. You want to ensure your CPU is compatible with faster memory types.
Luckily, both the Ryzen 7 2700 and the Ryzen 5 3600 are compatible with DDR4 RAM. DDR4 is the fastest type of RAM, even faster than its predecessor, DDR3. And it touts excellent overclocking speeds. For example, the RAM supported by these CPUs can run as fast as 2,933 MHz on the Ryzen 7 and 3,200 MHz on the Ryzen 5.
Ryzen 5 3600 supports faster RAM. However, high-speed RAM does come at the cost of higher energy consumption and latency (lag). But the numbers are very negligible.
Winner: Ryzen 5 3600
TDP
The Thermal Design Power (TDP) indicates how much heat the processor will dissipate. Generally, a lower TDP is preferred, as heat kills electronics. However, if you want a high-end CPU that can run at incredible speeds, you should expect a higher TDP.
Making a comparison between the Ryzen 7 2700 and the Ryzen 5 3600 is near impossible. That’s because both the CPUs have the same TDP at 65W. And they can reach a max temperature of 95 degrees Celsius.
Overall, the TDP seems quite normal for CPUs of this size and power. And since they’re both from the same company, we know that the TDP was calculated the same way and can be truly compared. If you have an issue with the temperature threshold, getting a decent cooling system is recommended.
Winner: Tie
Manufacturing Process
When designing a new processor, a lot of thought is put into the microarchitecture. Companies spend millions of dollars developing architectures. These become more efficient and practical with each generation.
AMD is the pioneer of its microarchitectures, codenamed Zen. The AMD Ryzen 5 3600 is based on the Zen 2 architecture. This microarchitecture was a breakthrough when it first came out. It helps reduce manufacturing defects and enables more cores to be built onto the same CPU. Additionally, this allows the Ryzen 5 3600 to hold up to 32 MBs of L3 cache.
As for the Ryzen 7 2700, it is built upon the Zen+ microarchitecture. Ironically, the Zen+ architecture is older than the Zen2 architecture. However, it has some exciting features, such as higher clock speeds and reduced thermal output. Additionally, it supports the Precision Boost 2 and XFR2 technologies.
However, due to the Zen 2 architecture’s superior processing speed and more capacious cache, it’s the clear winner here.
Winner: Ryzen 5 3600
Standout Features
Although both the Ryzen 7 2700 vs Ryzen 5 3600 have a lot in common, there are some stark differences.
Overclocking
Overclocking forces your CPU to process faster than it is intended to go. It’s useful for when you’re running power-demanding applications. While AMD employs automated overlocking mechanisms such as PBO and XFR, we’re interested in another technology.
And that’s the Ryzen 7 2700’s, Ryzen Master. It’s not a physical technology but software. Through this, you’re able to monitor overclocking as well as control the speed of your GPU. The UI is great and puts everything you need in one place.
AMD StoreMI Technology
One of the most astounding technologies featured on the Ryzen 7 2700 is the StoreMI technology. To put it in simple terms, it allows the user to expand and accelerate the onboard storage on your desktop. In addition, it effortlessly merges the speed of your SSD with the superior capacity of your HDD, provided you have both. This paves the way for more efficient storage, where you’re neither bound by your SSD nor your HDD.
AMD AES-Ni Technology
Intel developed the AES-NI technology. But many AMD processors also use it, such as the AMD Ryzen 5 3600 in question. It is an instruction set that enables improved speed of the applications and better data protection. Simply put, it uses a unique encrypting and decrypting protocol that keeps your data safe.
Conclusion
And that’s it for our Ryzen 7 2700 vs Ryzen 5 3600 comparison. While there is no clear winner, we can safely say the following:
Use the Ryzen 7 2700 CPU if you
- Need more all-around performance
- Are looking for faster loading speeds
- Need software for supervising overclocking
Use the Ryzen 5 3600 CPU if you
- Play games very often (due to better single core performance)
- Need more performance demands than an average home user
- Require better data encryption
