Are you looking for a new motherboard for your computer? We recommend that you pay attention to the chipsets they come with. Each chipset supports different features and offers different possibilities, so make sure to explore all options. In this article, we compare two Intel chipsets, Z370 vs Z390.
Z370 vs Z390 – Quick Comparison
Z370 and Z390 belong to Intel® 300 Series Desktop Chipsets. As such, these two chipsets are very similar. However, they do differ in some aspects, mostly due to the fact that they were not launched at the same time. Z370 was launched at the end of 2017, and Z390 at the end of 2019.
Keep on reading to find out what the exact differences are. Then you can make a decision on which chipset suits your needs better.
Intel Z370

Pros:
- Plenty of USB ports
- Supports DDR4 RAM
- Compatible with a variety of processors
- Supports CPU and RAM overclocking
Cons:
- No support for USB 3.2 Gen 2
- Supports only up to 64 GB RAM
Intel Z390

Pros:
- Supports USB 3.2 Gen 2
- Maximum RAM capacity of 128 GB
- Support both SLI and Crossfire
- Variety of form factors
Cons:
- Doesn’t support USB 3.2 2×2
- No support for PCI-e 4.0 or DDR5
Socket and CPU Compatibility
Socket Type Supported
Since they belong to the same Intel chipset series, Z370 and Z390 motherboards both support the same socket type. Each of them supports the LGA1151 socket (or Socket H4) that came after LGA 1150.
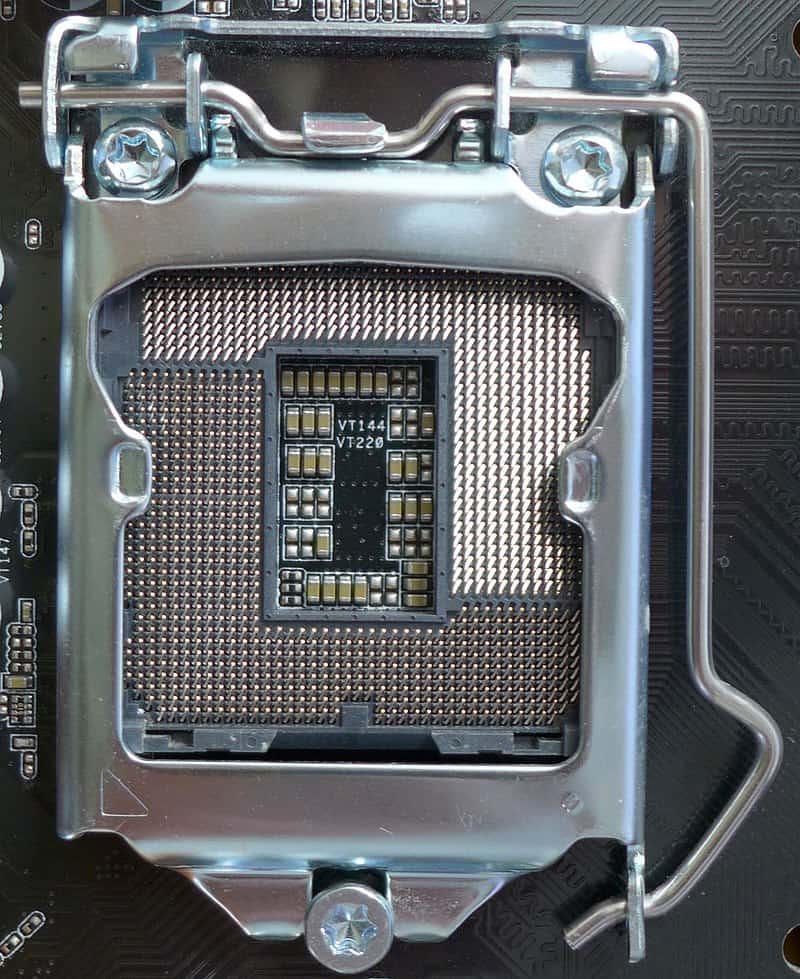
Why does socket type matter? To connect a processor and motherboard successfully, they both need to support the same socket type. So, you can’t connect an LGA1200-supporting motherboard with an LGA1151-supporting processor.
Since both chipsets in the Z370 vs Z390 comparison support LGA1151, they are compatible with the 8th and 9th Generation Intel Core processors.
CPU Support and Compatibility
These chipsets support the same type and generations of processors, as shown in the table below.
| Z370 Compatible Processors | Z390 Compatible Processors |
|---|---|
| 9th Generation Intel Core i9 Processors | 9th Generation Intel Core i9 Processors |
| 9th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors | 9th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors |
| 8th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors | 8th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors |
| 9th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors | 9th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors |
| 8th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors | 8th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors |
| 9th Generation Intel Core i3 Processors | 9th Generation Intel Core i3 Processors |
| 8th Generation Intel Core i3 Processors | 8th Generation Intel Core i3 Processors |
| Intel Pentium Gold Processor Series | Intel Pentium Gold Processor Series |
| Intel Celeron Processor G Series | Intel Celeron Processor G Series |
So, they support the 9th and 8th generation of Intel Core processors, as well as the Pentium Gold processors and Celeron G Series processors.
Form Factor
Unfortunately, motherboards don’t come in standardized shapes and sizes. They have different form factors, meaning they differ when it comes to size, shape, and design.
Why does this matter? Because you need different PC cases to place different motherboards. So, an ATX motherboard goes into the ATX case. Micro ATX motherboards can go into ATX and Micro ATX cases. Mini ITX can fit into all — ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini ITX cases.
Once you lock your motherboard form factor, it’s time to pay attention to the case. There is a classification of PC cases based on their size — Full Tower vs Mid Tower vs Mini Tower vs Small Form Factor Cases.

You also need to keep in mind that each form factor requires a different amount of power and hence different power supply units. Finally, they offer different connectivity options when it comes to PCI-e slots and RAM slots.
| Form factor | PCI-e slots | RAM slots |
|---|---|---|
| Mini ITX | 1 | 1 |
| Micro ATX | Up to 4 | Up to 4 |
| ATX | Up to 7 | Up to 4 |
Besides these three most common form factors, some manufacturers opt for a variation of the ATX form. The EATX or extended ATX form is its larger version that comes with more slots and requires more space.
In our Z370 vs Z390 comparison, both chipsets come in all form factors. So, depending on your needs, you can find a suitable form factor.
However, most of the motherboards come in ATX, but there is a significant number of motherboards with other form factors. Just keep in mind that larger form factors are usually more expensive.
For example, the Asus ROG Strix Z370-I Gaming is a Mini ITX motherboard, whereas ASUS ROG Maximus XI Extreme Z390 is an EATX motherboard.


GPU Compatibility
SLI / Crossfire Compatibility
Using multiple GPUs simultaneously on one motherboard is possible. However, the motherboard has to support it. The technology allowing multiple graphics card usage is called SLI or Crossfire.

There isn’t much difference between the two. They represent the same technology, but Nvidia calls it SLI, and AMD calls it Crossfire. If your motherboard supports either of these technologies, you can connect up to four graphics cards.

That way, you can have improved graphics on your computer. However, this enhancement comes with a cost. When using so many GPUs, the chances of overheating increase. Also, it can result in increased power consumption.
The chipsets in our comparison support either one or both of these technologies. Actually, most motherboards support both technologies. For example, ASUS ROG Strix Z390-E Gaming supports both SLI and Crossfire.

Performance
Overclocking
Computer component manufacturers set the speed limits of their products. From those specs, you can see the maximum speed limit these components can reach.
But in some cases, you can go over these set speeds. You can do that with the process called overclocking. Any component that has speed can potentially be overclocked. However, these components, including the motherboard, need to support overclocking.
The most overclocked computer components are CPUs and RAM. Luckily, both Z370 and Z390 motherboards support both CPU and RAM overclocking. However, some people claim that Z390 is slightly better at RAM overclocking.
Data Transfer Speed
Data transfer capabilities are very significant. Today, when we have so many devices, quick file transfer is a must. So, let’s compare these two chipsets when it comes to data transfer speeds.
| Chipset | 2.0 | 3.2 Gen 1 | 3.2 Gen 2 | Total number of USB ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z370 | 14 ports | Up to 10 ports | – | 14 |
| Z390 | 14 ports | Up to 10 ports | Up to 6 ports | 14 |
When comparing data transfer speeds, you need to take into account that different types of USB ports provide different speeds. USB 2.0 has a speed of 480 Mb/s, 3.2 Gen 1 has up to 5 Gb/s, and 3.2 Gen 2 provides a speed of up to 10 Gb/s.

Z370 and Z390 are the same when it comes to the total number of ports and the number of USB 2.0 and 3.2 Gen 1 ports. However, they differ when it comes to 3.2 Gen 2 ports since only Z390 has these USB ports.
Therefore, Z370 supports the speed of up to 5 Gb/s, and Z390 supports the speed of up to 10 Gb/s.
Memory Speed / Compatibility
These two chipsets are the same when it comes to the RAM type, the speed, and the number of DIMMs per channel. They both support DDR4 at speeds of up to 2666 MHz, and they support two DIMMs per channel.
However, they differ when it comes to the capacity of RAM. The maximum capacity of RAM on a Z370 motherboard is usually 64GB. There are also plenty of them that support up to 32 GB.
Z390, on the other hand, offers larger capacities. These motherboards usually support up to 128 GB, while a small number support up to 64 GB. So, Z390 is a much better choice when it comes to RAM.
Other Features
Wi-Fi Compatibility
Intel Z390 supports Intel Wireless-AC, an integrated wireless 802.11ac solution. A lot of Z370 and Z390 motherboards come with Wi-Fi support (mostly Wi-Fi 5 support). However, we encourage you to check this info for each motherboard you want to purchase. Sometimes manufacturers don’t include this feature, which is why you need to ensure it’s included.
Connectivity Options
The chipsets in our comparison are similar when it comes to connectivity options. You can expand your storage with up to six SATA ports on each of them. They both come with up to 24 PCI Express lanes, and both support PCI-e 3.0.
| Connectivity Options | Z370 | Z390 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of USB ports | 14 | 14 |
| Transfer Speed | Up to 5 Gb/s | Up to 10 Gb/s |
| SATA 6.0 Gb/s Ports | 6 | 6 |
| PCI Express Lanes | 24 | 24 |
| PCI Express PortConfigurations | 1×16 or 2×8 or 1×8+2×4 | 1×16 or 2×8 or 1×8+2×4 |
| Ethernet | Yes | Yes |
The PCI Express port configurations are also the same when it comes to both chipsets. However, the biggest difference is in USB data transfer speeds. Z390 offers up to 10 Gb/s, whereas Z370 offers only up to 5 Gb/s.
BIOS
Sometimes, motherboards require a BIOS update in order to run properly. If you have a motherboard with an Intel 300 series of chipsets, you might need a BIOS update, as well. If you have the 8th generation of Intel Core processor, you probably don’t need an update.
But, if you want to boot the 9th generation of Intel Core processors, Intel recommends that you update your BIOS.
Future Proofing
In terms of future-proofing, Z390 stands a little better since it offers faster data speeds of up to 10 Gb/s. Also, it supports up to 128 GB RAM, while Z370 offers only up to 64 GB.
Recommended Z370 Motherboard
Asus Prime Z370-A
Asus Prime Z370-A comes with the LGA 1151 socket compatible with the 9th and 8th Gen Intel Core processors. It supports up to 64 GB DDR4 RAM. It is both Crossfire and SLI capable.
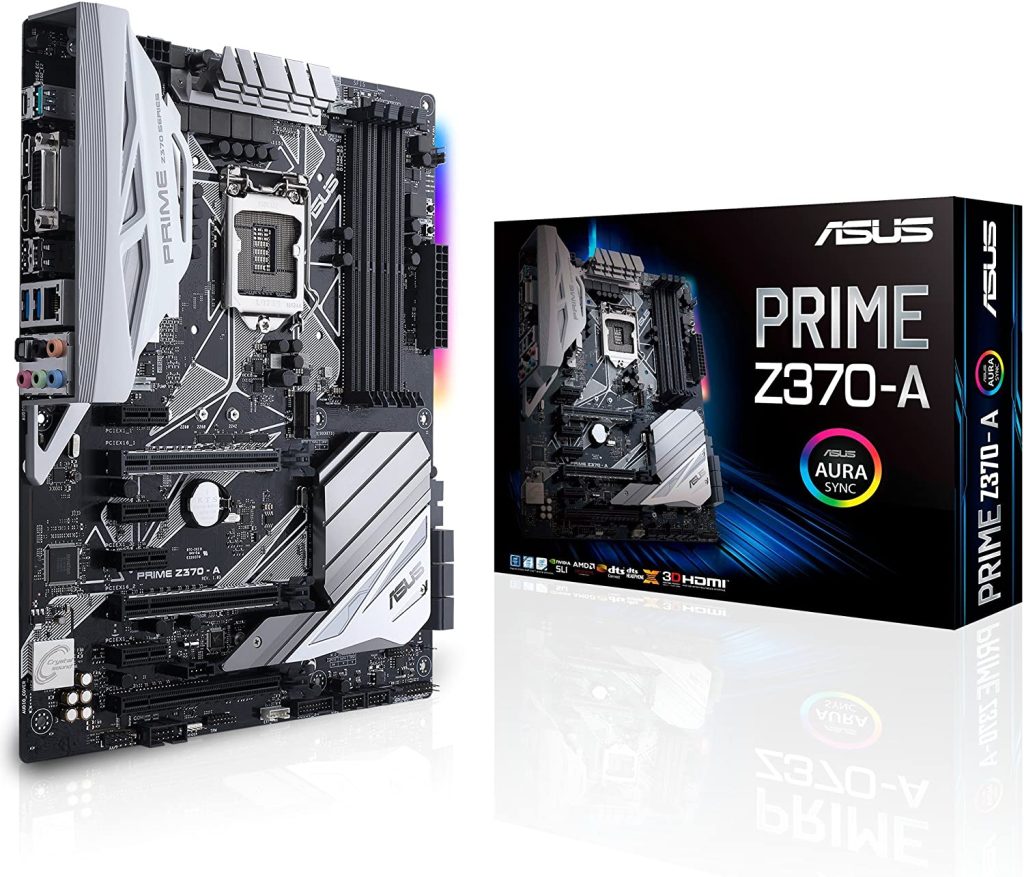

In total, it has three PCIe x16 slots. The form factor of this motherboard is ATX.
Recommended Z390 Motherboard
Gigabyte Z390 UD
The Gigabyte Z390 UD ATX motherboard offers a lot of fantastic features. First of all, it is compatible with the 9th and 8th Gen Intel Core processors and supports up to 128 GB DDR4.
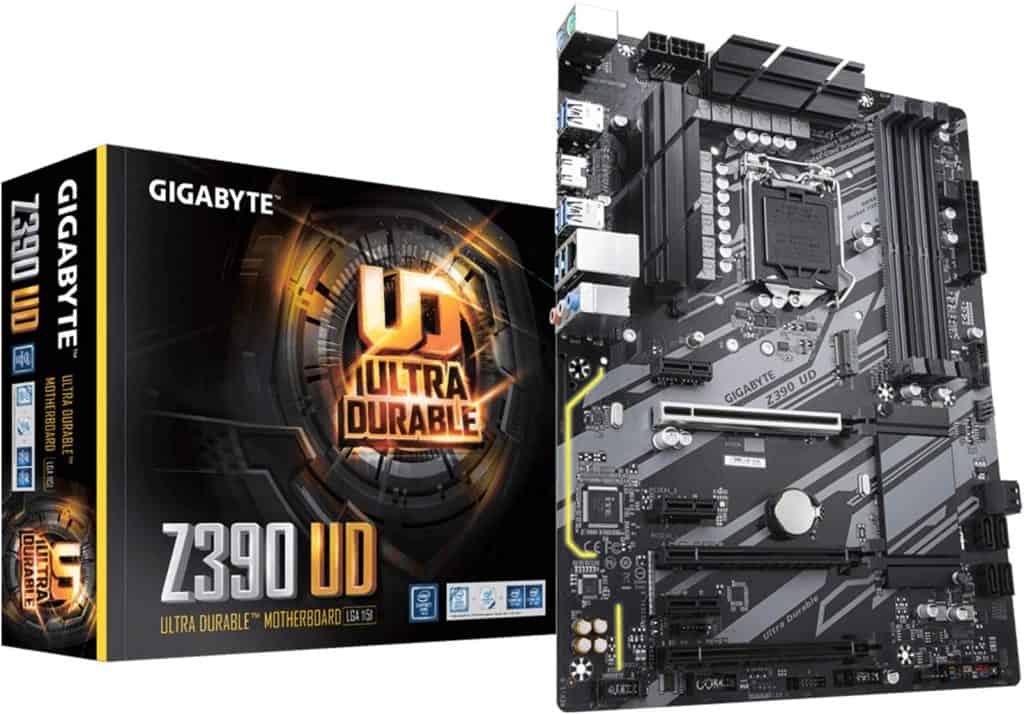

It has three PCI Express x16 slots in total. Multiple GPUs are also possible on this motherboard via Crossfire technology.
Conclusion
To conclude this Z370 vs Z390 comparison, let’s emphasize the best features they offer.
Z370 chipset offers a lot of features. If you want a motherboard that supports overclocking, Z370 supports both CPU and RAM overclocking. You have a variety of form factors and compatible CPUs you can choose from.
If you are looking for large RAM capacity, Z390 is a great choice since it supports up to 128 GB DDR4. It also offers a fast data transfer speed of up to 10 Gb/s and a lot of PCI-e 3.0 lanes. Most Z390 motherboards also support SLI and Crossfire technology, so you can run multiple GPUs.