Looking for a new motherboard? Are you overwhelmed with all the information you encountered? Don’t worry; you’re not the only one! Motherboards are essential computer components, they support a lot of features, and it can get complicated to pick one. But we are here to teach you all about motherboards — and in this article, we compare Z590 vs X570 chipsets. So, let’s see what they offer.
Z590 vs X570 – General Overview
Chipsets in this comparison are made by different manufacturers. Intel is the manufacturer of the Z590 chipset, whereas X570 is an AMD product.

Since they come from different manufacturers, they differ in many ways. For example, they have different sockets and support different CPUs. However, they also have a lot in common. So, keep reading to find out more about their differences and similarities.
Intel Z590

Pros:
- Variety of compatible CPUs
- PCIe 4.0 support
- High data transfer speed – 20 Gb/s
- Maximum memory capacity of up to 128 GB
Cons:
- Only six SATA ports
- Memory speed only up to 3200 MHz
AMD X570

Pros:
- Supports up to 4400 MHz DDR4 RAM
- Comes with up to 14 SATA 6 Gp/s ports
- 36 PCIe lanes
- Supports overclocking
Cons:
- Data transfer speed only up to 10 Gb/s
- Doesn’t support DDR5 or PCIe 5.0
Socket and CPU Compatibility
Socket type supported
Since these two chipsets come from different manufacturers, they use different socket types to connect the motherboard and CPU.
Intel Z590 chipsets come with an LGA 1200 socket type, which means it is compatible with the 10th and 11th generation of Intel Core processors.
X570 chipsets are manufactured by AMD, and therefore, they support the AM4 socket type.
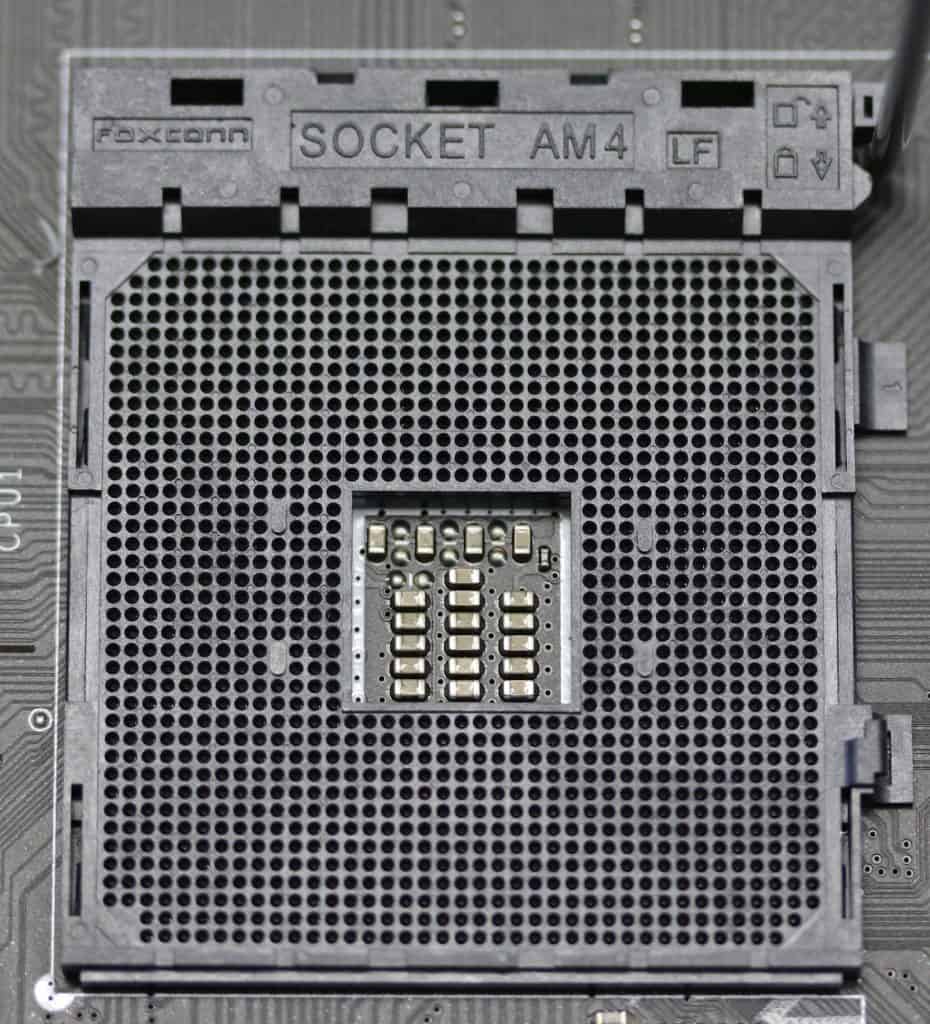

CPU support/compatibility
As we mentioned above, CPUs and motherboards need to be compatible in order to run properly. So, let’s check out the table below to see which CPUs the chipsets in our Z590 vs X570 comparison support.
| Z590 Compatible Processors | X570 Compatible Processors |
|---|---|
| 11th Generation Intel Core i9 Processors | AMD Ryzen 2000 |
| 10th Generation Intel Core i9 Processors | AMD Ryzen 3000 with Radeon Graphics |
| 11th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors | AMD Ryzen 3000 |
| 10th Generation Intel Core i7 Processors | AMD Ryzen 4000 |
| 11th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors | AMD Ryzen 5000 |
| 10th Generation Intel Core i5 Processors | |
| 10th Generation Intel Core i3 Processors | |
| Intel Pentium Gold Processor Series |
So, Z590 motherboards support the 11th and 10th generation of Intel Core processors, as well as the Pentium Gold series. X750 motherboards support AMD Ryzen 2000 all the way up to AMD Ryzen 5000 series.
Form Factor
Each motherboard has its own form factor that represents its shape, size, and design. There are several motherboard form factors — the most common are Mini ITX, Micro ATX, ATX, and EATX. The EATX is the largest, and Mini ITX is the smallest.
The most obvious difference between these form factors is the size. For example, Mini ITX is 6.7 x 6.7 inches in size, whereas the EATX motherboard is 12 x 13 inches large. Since they differ in size, they need a different computer case according to their size.
Bear in mind that larger motherboards need more power and a better cooling system since they generate more heat. Also, expect to cough up extra money for a larger motherboard. But in return, you will get features like overclocking, multi-GPU support, and more PCI-e and RAM slots.
In our chipset comparison, the majority of motherboards have an ATX form. However, there are plenty of other form factors as well. So, you have a variety of choices when it comes to both of these chipsets.
GPU Compatibility
SLI / Crossfire compatibility
Did you ever want to use more than one graphics card to enhance computer performance? If you did, you should know that there is a technology enabling this process. It is called SLI or Crossfire.
They are practically the same technologies with minor differences. SLI is Nvidia’s product, whereas Crossfire is a product of AMD.
SLI might cost a little bit more since it requires a paid license. SLI also requires the same graphics card model and the same memory. Crossfire is less demanding since it needs only the same architecture.
Either way, you can connect up to four graphics cards on one motherboard. But you need to have free PCIe x16 slots.
Both chipsets in our comparison support these technologies. Some motherboards, such as X570 Asus ROG Crosshair VIII Dark Hero, support both SLI and Crossfire technologies.
Performance
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of pushing a computer component frequency over its factory limit. People opt for overclocking when they want to enhance performance without investing in new parts. The reason usually comes down to the ability to run demanding games or computer programs.
Many computer components, such as graphics cards, memory, and CPUs, can be overclocked. However, don’t expect just any component to be unlocked for overclocking. The motherboard needs to support overclocking.
Luckily, both Z590 and X570 motherboards support overclocking. So, if you plan to use this feature, you can go with either of these chipsets.
But bear in mind that overclocking comes with some disadvantages. Since you push the components over their limits, you might face overheating problems. So, it might be a good idea to invest in an advanced cooling system.
Besides overheating, another problem you could encounter is the shorter lifespan of your components. Lastly, be aware of the fact that manufacturers usually don’t cover damage to computer parts caused by overclocking.
Data transfer speed
There are different types of USB ports depending on their speed. So, there are ports with speeds of 480 Mb/s (USB 2.0) and all the way up to 20 Gb/s (USB 3.2 Gen 2×2). Let’s see how Z590 and X570 chipsets stand in this segment.
| Chipset | USB 2.0 | USB 3.2 Gen 2×1 | USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Z590 | 14 ports | Up to 10 ports | Up to 3 ports |
| X570 | 4 ports | Up to 12 ports | – |
Z590 supports the fastest USB port — USB 3.2 Gen 2×2. And it has up to three of these ports. X570, on the other hand, doesn’t support this USB generation. But comparatively, it has more USB 3.2 Gen 2×1 ports.

By comparison, Z590 supports USB speeds of up to 20 Gb/s. X570 supports USB speeds of up to 10 Gb/s.
Memory speed and Compatibility
These chipsets support DDR4 RAM type. In terms of memory capacity, most Z590 and X570 motherboards have a maximum capacity of up to 128GB. However, there are some motherboards with a capacity of up to 64GB, mostly due to the fact that their form factor is Mini ITX.
These two chipsets differ when it comes to memory speed. Z590 supports a speed of up to 3200 MHz. X570 is better in this segment since it supports up to 4400 MHz.
Other Features
Wi-Fi compatibility
Some motherboards have built-in Wi-Fi, which is a great feature if you don’t want to deal with cables. Z590 comes with Wi-Fi 6 support. X570 motherboards also support Wi-Fi connectivity.
However, we strongly recommend that you check whether the motherboard you intend to buy supports Wi-Fi. Even though these chipsets allow built-in Wi-Fi, sometimes manufacturers don’t include it in their motherboards.
Connectivity options
The maximum USB speeds are not the same on these chipsets. Z590 is better in this segment since it supports USB 3.2 Gen 2×3. That means that it supports USB speeds of up to 20 Gb/s. X570 supports only up to 10 Gb/s.
| Connectivity Options | Z590 | X570 |
|---|---|---|
| Transfer Speed | Up to 20 Gb/s | Up to 10 Gb/s |
| SATA 6.0 Gb/s Ports | 6 | 14 |
| PCI Express Lanes | 24 | 36 |
Z590 has six SATA 6 Gb/s ports, whereas X570 has up to 14 SATA ports. Another segment where these two chipsets differ is the number of PCIe lanes. Z590 has 24 lanes, whereas X570 has up to 36 PCIe lanes. However, they both support PCI-e 4.0.
BIOS
Sometimes, a BIOS update is needed to fix the bugs or to support new hardware. Z590 and X570 motherboards might require a BIOS update. For example, when you install Ryzen 5000 or 4000 series CPU on an X570 motherboard, you might not need an update. But if you get older CPUs, you will most probably need to update your BIOS.
Future-proofing
Although both of these chipsets offer great features, they can’t really be labeled as future-proof. It is true that Z590 supports up to 20 Gb/s data speed, and X570 supports RAM speed of up to 4400 MHz. They both support PCI-e 4.0, as well. However, neither of these chipsets support DDR5 or PCI-e 5.0.
Recommended Intel Z590 Motherboard
Asus ROG STRIX Z590-E GAMING WI-FI
Asus ROG STRIX Z590-E GAMING WI-FI is an ATX motherboard with an Intel Z590 chipset. It supports up to 128 GB of DDR4 RAM via four memory slots. Integrated cooling options can be optimized via UEFI BIOS or Fan Xpert 4. It has six SATA ports and two USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 ports, one at the rear and one at the front.
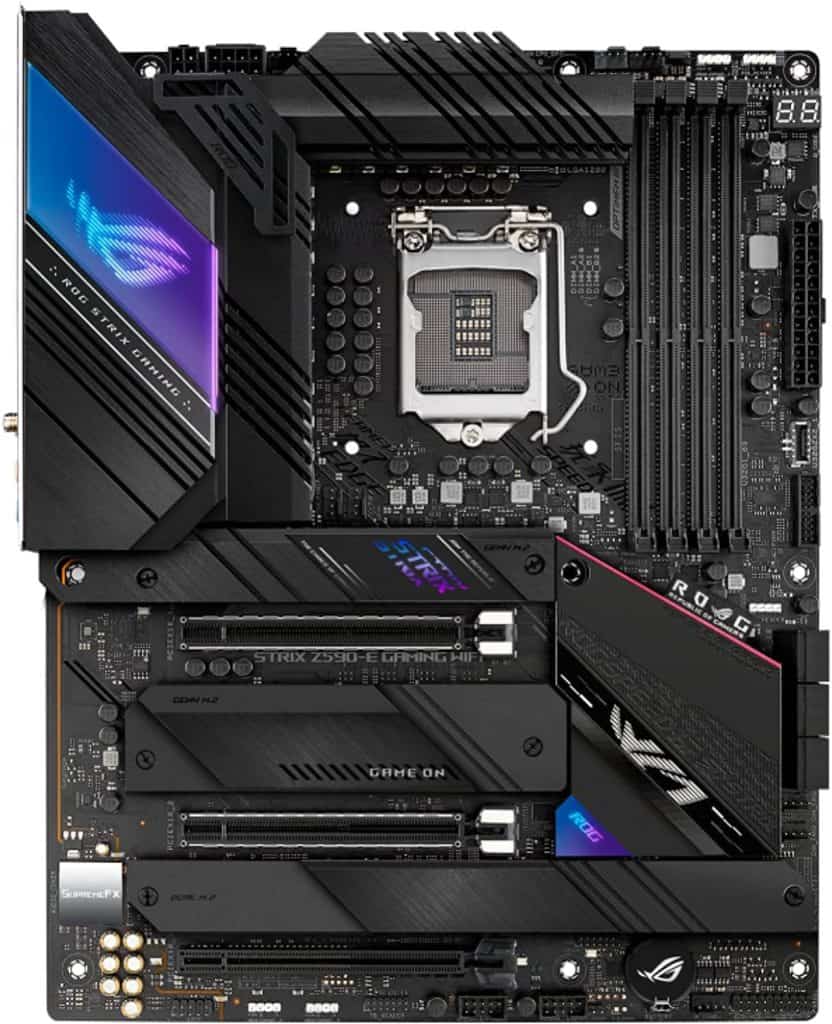

If you get this motherboard, you can count on PCIe 4.0 support, Intel Wi-Fi 6E and dual onboard 2.5 Gb ethernet. You can also use SLI technology because the motherboard supports it. Additionally, it has three PCI-e x16 slots.
Recommended Intel X570 Motherboard
Asus TUF GAMING X570-PLUS (WI-FI)
Asus TUF GAMING X570-PLUS (WI-FI) ATX motherboard also supports up to 128 GB DDR4 memory via four DIMMs. With two PCIe x16 slots and Crossfire support, you can enjoy the benefits of running multiple GPUs.
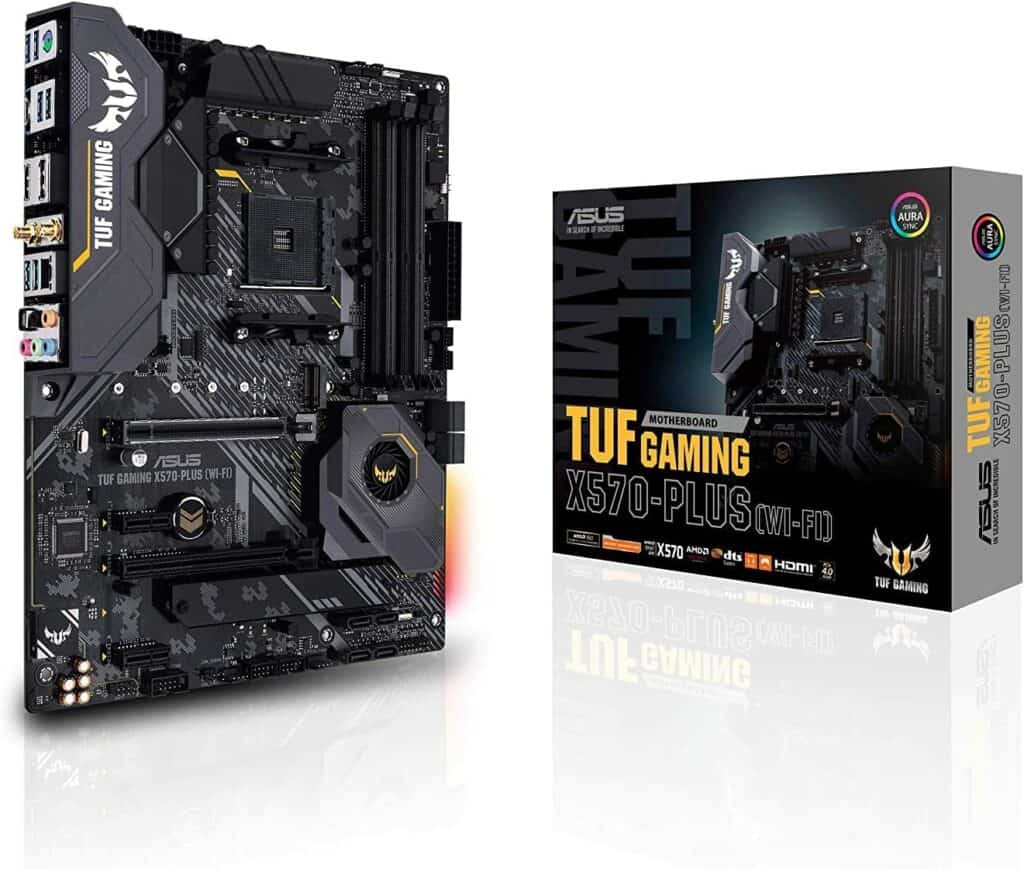

It has three USB 3.2 Gen 1 ports (up to 10Gbps) and eight SATA 6 Gb/s connectors. It also supports PCI-e 4.0, Wi-Fi 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac, and dual-band frequency 2.4/5 GHz.
Conclusion
So, which chipset prevails in this Z590 vs X570 comparison? It mostly depends on your needs. They both support DDR4 memory with a maximum capacity of up to 128 GB, and overclocking and SLI/Crossfire technologies.
Z590 excels at USB speeds since it supports USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 with speeds of up to 20 Gb/s. They are compatible with various processors and come in different form factors.
X570 supports memory speeds of up to 4400 MHz. These motherboards come with plenty of SATA and USB ports and up to 36 PCIe lanes. They support overclocking features and usually support Wi-Fi.
Which one did you pick? Let us know in the comments!