If you’re in the market for a new TV and you’re looking to invest in a premium viewing experience, you’ve likely come across the terms QLED and OLED.
While both of these technologies are innovative in their own right, you certainly won’t be disappointed with either one. However, there are some significant differences between the two that you should take into consideration. The technology you choose to go with will likely depend on your priorities and needs regarding viewing experience, space, intended use, viewing angles, and more.
There might not be an obvious winner in this comparison, but read our OLED vs QLED article and discover which panel technology is better for you!
OLED vs QLED Introduction
QLED stands for Quantum Light-Emitting Diode and it’s an upgrade over existing LED technology.
These displays use an LCD backlight (just like a regular LED TV does) but they introduce a quantum dot color filter in front of this backlight to produce a broader range of colors and improve contrast.
A big champion of QLED technology is Samsung – the tech giant exclusively produces QLED displays and stands as a competitor to OLED. Other manufacturers like Hisense and TCL also make QLED displays, although Hisense has also been producing OLEDs in the past few years.
QLED Pros
- Greater brightness and color vibrancy
- Generally more affordable
- Available in all sorts of dimensions
- More reliable, tested technology
QLED Cons
- Worse black levels and contrast
- Worse viewing angles and flexibility in general
Although OLED stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diode, the LED part of the acronym doesn’t hold true in quite the same way as it does for regular LED or QLED TVs.
Unlike regular LED and QLED displays, OLED doesn’t have a backlight. Instead, each pixel produces its own light in OLED displays, which provides better contrast and a dominating performance in black levels.
Currently, LG Display is the only company that makes OLED displays. However, they do sell it to other tech manufacturers, so you’ll see OLED displays in Panasonic, Sony, Phillips, and other brands’ offerings.
OLED Pros
- Better contrast and black levels
- Wider viewing angles
- Quicker response rate
- Newer, cutting-edge technology
OLED Cons
- More expensive
- Available only in larger sizes
What is QLED Technology?
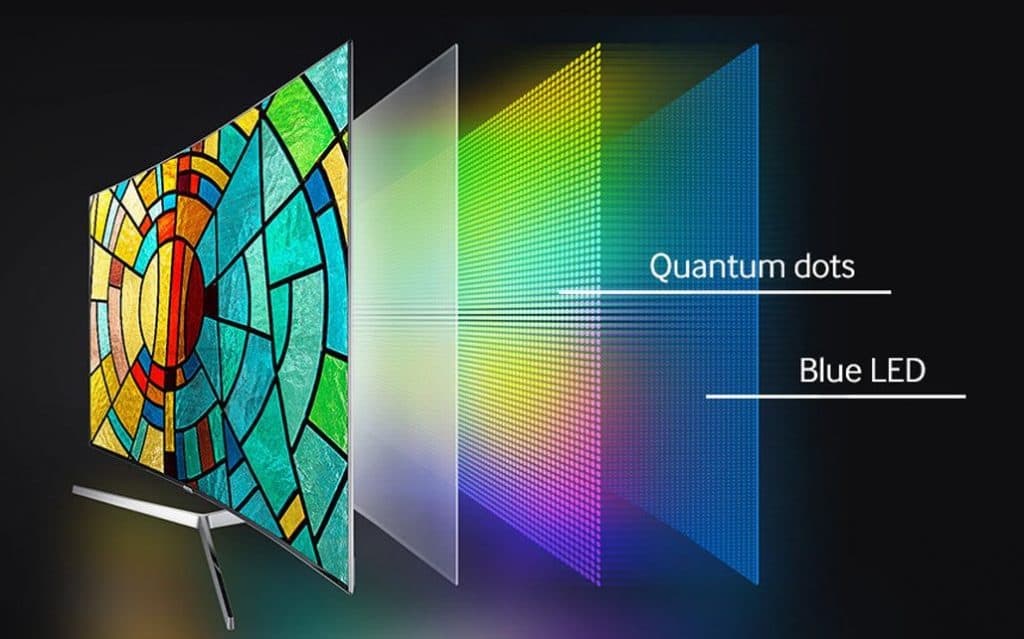
QLED is a panel technology that Sony first developed in 2013. However, this technology is attributed today to Samsung since it has perfected it and rebranded it in 2017 to the name we’re now all familiar with.
In reality, Samsung has been working on improving its LED technology by introducing quantum diodes since 2015. The name QLED is more of a marketing move than a ground-breaking technology effort.
How does it work?
If you understand how a regular LED TV works, you’re pretty close to understanding QLED technology.
An LED display uses diodes – semiconductor devices that emit visible light when electric currents pass through them. These light-emitting diodes are usually placed on a panel inside your TV that is in charge of producing the colors, brightness, and contrast – essentially everything you see on the screen.
What QLED technology did was introduce a quantum dot layer over the LCD panel that enhances the image by providing better contrast and more subtle colors. QLED displays can significantly boost the capabilities of HDR and 4K images, which is why a lot of people are excited about this new technology – even if it’s not incredibly ground-breaking.
Advantages of QLED over other technologies
QLED can help you get the most out of your 4K TV by enhancing color vibrancy and contrast. Compared to standard LED technology, QLED provides a much better viewing experience that almost seems as if you’re increasing your resolution (even though a 4K LED and a 4K QLED TV have the exact same screen resolution).

Compared to OLED displays, QLED gives you better brightness, especially in well-lit environments. There are also a lot of QLED models to choose from, all coming in various dimensions and looks.
Disadvantages of QLED compared to other technologies
QLED is hardly on the cutting edge of TV technology, especially when compared to OLED.
It does signify a big move by Samsung and, while it’s a step in the right direction, it’s an upgrade over the current LED technology, carefully crafted with marketing messaging.
Some of the issues that standard LED TVs have – an unconvincing black range, light bleeds, bad viewing angles, etc. – remain unsolved with QLED.
What is OLED Technology?
Curiously, OLED TV technology was also introduced by Sony in 2008 – maybe Sony is the real hero of the TV industry.
Today, this panel technology is pioneered by LG Display and sold not only by their sister company, LG Electronics, but also by other players in the tech industry.
How does it work?
As mentioned, OLED doesn’t use a backlight: the light in these TVs is emitted by each individual pixel. This means that a bright, colored pixel can appear next to a black one with zero color bleeding that we’re used to seeing in regular LED TVs.
When you’re watching a dark scene on a QLED display, what’s actually happening from a technical perspective is the LED lights in the panel are being dimmed or turned off to simulate darkness. Since this same backlight provides color and contrast for the entire scene, the whole screen will be dimmed, and you won’t be able to make out a lot of the scene.
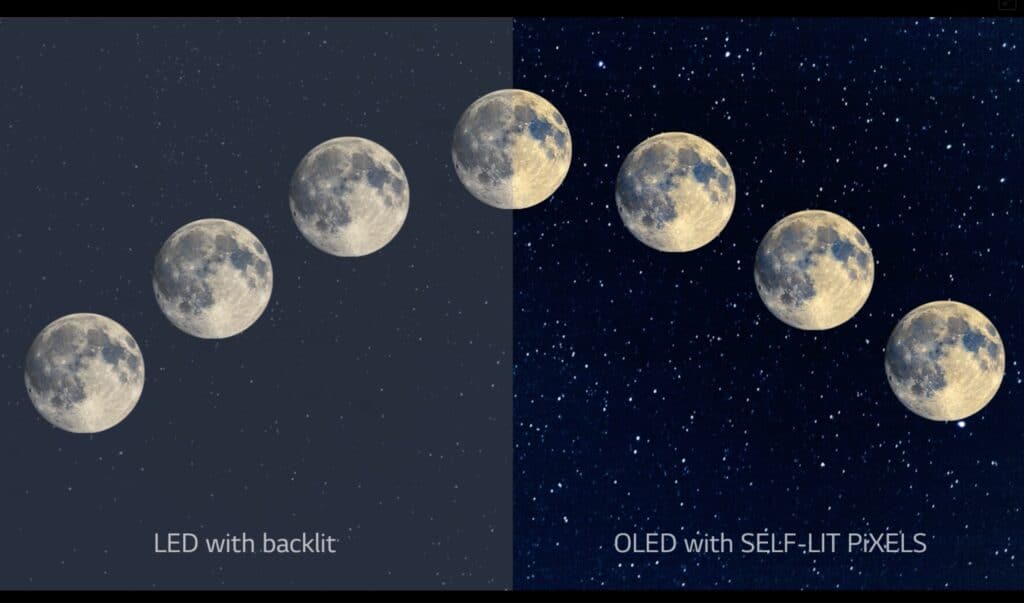

When watching this same scene on an OLED display, individual pixels are being turned off to simulate darkness. However, all other pixels next to these dark ones are still appearing as they should be, so the scene will be more nuanced and vibrant.
In simpler terms, OLED displays provide much better color separation and contrast, especially when it comes to black levels.
Advantages of OLED over other technologies
OLED is a genuine advance in TV display technology. Apart from the most obvious advantage in black levels and contrast, these screens are lighter, more flexible, and provide better viewing angles.
The lack of a backlight also makes OLED displays easier on the eyes and more power-efficient.
Disadvantages of OLED compared to other technologies
Since OLED has no backlight, these displays tend to be a little darker than QLED and even regular LED TVs. If your TV is in a living room that gets lots of daylight, watching your favorite movie in the daytime might not be a perfect experience.
OLED displays are also typically more expensive, especially when we get to the larger screens.
What’s better QLED or OLED?
Now, to finally answer our question: is there a clear winner between QLED vs OLED?
Let’s see how they compare in all of the important categories.
Brightness
Screen brightness is an important factor when comparing displays – this is something you’re probably well aware of if you’ve ever tried reading a text message on a poorly lit smartphone during the summer.
The crucial difference between QLED and OLED displays (one has a backlight, the other doesn’t) comes into play here. OLED’s light-emitting pixels can’t really be compared to QLED’s panels that emit much more light and give brighter hues and more vivid colors.

QLED is the clear winner here, providing much more brightness and a wider range of better-saturated colors than OLED. Although OLED has improved in this area in the past few years, it still has a long way to go to stay competitive, especially in daylight conditions.
Contrast and black levels
Contrast refers to the range between the darkest and brightest portions of a single image. Screens with higher contrast generally produce a darker lower spectrum while also giving a lot of variety in the bright ends.
The complexity of the black levels on OLED screens is still unmatched (and, by design, almost impossible to match) by QLED displays. Since a QLED display needs to dim the diodes to achieve darkness, the light from the remaining diodes will often spill onto the black sections.
OLED displays simply offer better contrast and more precise black levels due to their innovative design.
Sizes and variety
One thing you always want to see when you’re choosing a new TV is variety, both in terms of size and price.
This is one area where QLED TVs seem to outshine (no pun intended) OLEDs since the technology is more cost-effective to produce. You’ll find lots of expensive, big-screen QLED TVs on the market, as well as some smaller, relatively affordable options. OLED TVs, on the other hand, are harder to find in the low-to-mid-range. Up until recently, it was even hard to find an OLED TV under 50’’.
If you’re looking for variety and you don’t want to just splurge on a big-screen TV, QLED is the better choice.
Response time and refresh rate
Response time refers to the amount of time a TV or monitor requires to change the properties of any given pixel – its color, brightness, etc. – measured in milliseconds.
This is a metric that a lot of gamers and movie buffs look at when comparing two displays. Lower response time and refresh rates result in a crisper image that can make a big difference when you’re playing a game or watching a new Marvel movie.
Although QLED displays are certainly no slouches in this category, OLED wins with consistently lower response times. QLED displays usually have response times between two and eight milliseconds, while OLEDs can go well below two milliseconds (to about 0.1ms).
Viewing angles
If you’re looking for a TV for cinema nights with your friends and family, viewing angles will be of great importance. Naturally, you want the people sitting on the sides to have the same experience as those right in front of the TV.

Here, again, QLED’s backlight panel works against it, affecting viewing angles and even appearing discolored for users sitting on the outside viewing areas. The panel simply lights the screen differently in different areas.
OLED displays are the clear winner in this category, allowing for incredible viewing angles of up to 84 degrees. Their self-emissive pixels make for almost perfectly uniform screens, wherever you’re watching from.
Reliability and durability
While we can’t make broad claims about the durability or lifespan of QLED or OLED displays as entire categories, certain things can point us in the right direction.
We know that the LED diodes, while not particularly innovative, have been around for years. They’re reliable and have a proven track record when it comes to longevity and reliability. That isn’t to say that all QLED TVs will be durable (especially not the cheaper ones), but the underlying technology is tried and tested.
On the other hand, OLEDs use organic materials, and like all organic matter, their diodes are destined to decay over time. In that sense, they pretty much have a set expiration date that will vary from model to model.
QLED is the more reliable, safer option, although OLED displays are far from unreliable or erroneous.
Power consumption
Your TV might not be a big power consumer in your household – although large, very bright screens will take their toll on your electricity bill, especially if used frequently.
Once again, the very design of these two types of panels dictates the power consumption.
As you might have assumed by now, QLED TVs consume more power than OLEDs due to their panels that emit light. This light requires electrical energy and generates more heat. All of this contributes to a higher energy profile.
OLED displays don’t need a bright backlight, so they’re more power-efficient.
Eyestrain and health
This may be a minor point but, as digital devices and screens are becoming more prevalent in our society, the awareness about their effects on our health is slowly growing.
Amid this discussion lies a question about blue light. It has long been suggested that prolonged exposure to blue light has adverse effects on our vision, with lots of products being marketed as potential solutions – from glasses to blue light filters.
However, the evidence to support these claims is still lacking.
If we were to accept the theories about blue light, OLED TVs would be the better choice since they emit less than a third of blue light compared to QLED and LED TVs that use a backlight.
Even if these theories aren’t true, there are other ways in which blue light can affect your life, including messing with your circadian rhythm. Switching to OLED displays might help you alleviate some of these concerns.
Price
It goes without saying that the prices will vary depending on the specific model and dimensions. For example, you’ll find lots of OLED TVs at around the $1,300 price, but they can quickly go up to $10,000 if you’re looking for a premium, big-screen model.
However, we can safely say that more variety and better deals are found in the QLED space. Hisense makes some very affordable QLED TVs, which can end up around the $500 mark.
Generally, QLED displays are more affordable because the technology is cost-effective to produce and more massively adopted. We can expect OLED TVs to keep dropping in price (which has already been happening to an extent), but QLEDs are the more budget-friendly option.
QLED vs OLED in the Future
Lastly, let’s take a moment to peek into the future of these technologies and think about what we may see from their key manufacturers going forward.
As for Samsung and their QLED technology, the main challenge is to deliver better black levels that could match those of OLED. To do this, the manufacturers are working on mini-led and even micro-led technologies that would provide more control over backlighting. In other words, the new QLED TVs might be fitted with thousands of small LEDs (instead of hundreds), coming quite close to what OLED is already doing with their self-emissive pixels.
The key issues that LG Display is working on with their OLED technology are brightness levels and production costs. While we’ve seen movement on both of these fronts, their performance in well-lit environments is still questionable, and so is their competitiveness with QLED TVs in the lower range.
Conclusion
Naming a clear winner in our OLED vs QLED comparison isn’t so straightforward – each technology has its advantages, and different users will find different features appealing.
If you’re looking for an all-purpose TV with excellent picture quality, vibrant colors, and high brightness levels at a relatively small cost, QLED is the better choice. It will give you great results that will significantly outperform your regular LED TV and look great in all kinds of environments.
If you consider yourself a performance-oriented user looking for the latest cutting-edge technologies, you should be looking at OLED. The difference in black levels will be instantly noticeable to someone who appreciates top-notch video quality and considers themselves a cinephile. Wider viewing angles, power-effectiveness, and response times will also contribute to an impressive viewing experience.
