AMD and Intel have been battling it out in the CPU industry for over a decade – they offer competing products in almost all market segments, at almost all price points.
Nowhere is that more evident than with AMD’s Ryzen 5 2600 and Intel’s i5 9400F. The margins between these two CPU units are pretty fine so you’ll have to look deep into their specs and compare them to your particular needs to find a clear winner.
As you’re about to see, the Ryzen 5 might edge out the i5 9400F but it still largely depends on what kind of tasks you’re planning to run.
So, here is our detailed Ryzen 5 2600 vs i5 9400F comparison!
Ryzen 5 2600 vs i5 9400F – The basics
Released in Q2 of 2018, the Ryzen 5 2600 is a part of AMD’s second-generation of mainstream desktop processors. It supersedes the Ryzen 5 1600 and is a clear upgrade in all important areas like stock base/boost clock and memory latency.

Pros:
- High base clock speed
- More threads allow for more efficient multitasking
- Supports faster memory which can give quicker system performance
- Can be overclocked
Cons:
- Not as good single-core performance
- More expensive
The i5 9400F is a 9th generation Coffee Lake desktop processor released in Q1 2019. It’s a 6-core processor that can go up to 4.10 GHz without overclocking, through Intel’s signature Turbo Boost Technology.

Pros:
- Better single-core performance
- Lower memory latency allows for faster computations and quicker data retrieval
- Higher max temperature before failure
- More recent
Cons:
- Can’t be overclocked
- Fewer threads mean it’s not as effective when executing multiple tasks simultaneously
| Features | Ryzen 5 2600 | i5 9400F |
|---|---|---|
| Launch date | 04/19/2018 | 01/07/2019 |
| Product family | AMD Ryzen™ 5 Desktop Processors | 9th Generation Intel® Core™ i5 Processors |
| Number of cores | 6 | 6 |
| Number of threads | 12 | 6 |
| Base clock | 3.4 GHz | 2.90 GHz |
| Max turbo clock | 3.9 GHz | 4.1 GHz |
| Can be overclocked | Yes | No |
| Max temperature | 95oC | 100oC |
| RAM speed | 2933MHz | 2666MHz |
| L1 cache | 576KB | 384KB |
| L2 cache | 3MB | 1.5MB |
| L3 cache | 16MB | 9MB |
| TDP | 65W | 65W |
| Price | Check Price on Amazon | Check Price on Amazon |
Key Specifications
Now, let’s get to comparing the key specifications of these two CPUs and see which one comes out on top!
Cores and core performance
Cores are the most important hardware components of a processor. More cores usually equal higher clock speeds and increased performance.
Ryzen 5 2600 and i5 9400F are both hexa-core (6-core) processors so they’re tied in this regard – this is one of the reasons why the two are so close performance-wise. However, the i5 9400F has better single-core performance, as evidenced by benchmark tests.
When we get to dual-core and quad-core performance, Ryzen 5 2600 is more powerful and has better marks in most tests.
Now comes the logical question: what’s more important, single-core or multi-core performance? This depends on the applications you’ll be running, as some apps use multiple cores while others run on a single one. For example, it’s typically considered that single-core performance is more important for gaming.
So, in terms of cores and core performance, it’s pretty much a wash between these two CPUs. We might give a slight edge to Ryzen 5 2600 since most modern programs will use multiple cores – including many new (and almost certainly, future) games.
The number of threads
We can’t only talk about core performance without discussing threads. When combined, these two components are among the most important factors that determine the computing power of a CPU.
The relationship between cores and threads is a complicated one for the casual tech fan. Put simply, CPU cores are the actual hardware component of a processor while threads are the virtual components that manage the tasks.
In this relationship, cores always outweigh threads. In other words, a processor with 8 threads and 8 cores will significantly outperform one with 8 threads and 4 cores.
Threads don’t carry as much weight but they aren’t insignificant either. Since Ryzen 5 2600 has double the threads of the i5, we can consider it a clear winner in this area.
The all-important question – clock speed
Other than cores and threads, clock speed is probably the most well-known performance indicator in CPUs.
In layman’s terms, a processor’s clock speed signifies the number of operations that a processor can execute in a single second, measured in GHz (gigahertz).
When it comes to base clock speed (think of “base” as “default”), Ryzen 5 2600 again outperforms the i5 9400F with 3.4 GHz compared to 2.9 GHz. Both of these processors can increase their clock speed if needed but we’ll get to that later on.
Which sockets do they use?
Compared to some other features and specs in this article, sockets are relatively unimportant when choosing the best CPU.
These are pretty much the only reasons why you might want to consider them:
- A CPU you like might not be compatible with the motherboard you already have;
- You might be choosing your motherboard based on the CPU. In other words, you might want to get a motherboard that’s more likely to be compatible with the next CPU generations.
The Ryzen 5 2600 uses the AM4 socket while the i5 9400F uses a socket called LGA 1151.
Ryzen is, once again, at a slight advantage here simply because the AM4 socket hasn’t been surpassed by the AM5 (yet). So, a motherboard with an AM4 socket will be more future-proof than the LGA 1151 which has already been surpassed by the LGA 1200.
Who offers more cache?
Your CPU usually pulls data from the RAM memory on your PC but data that it accesses frequently will be stored in the CPU’s cache memory. Think of this cache as a small memory slot that’s stored on the processor for easier and quicker access to data.
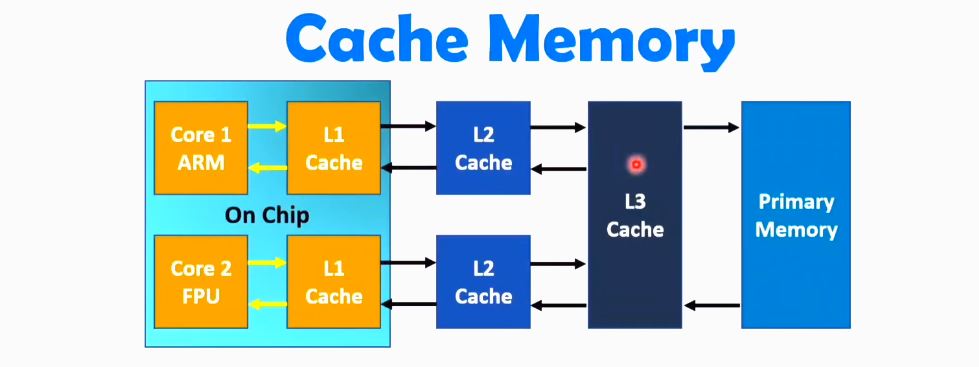
More cache will typically make the processor faster, reducing the time and energy required for data access.
Ryzen 5 2600 has more cache on all three levels compared to the i59400F:
- L1: 576KB vs 384KB
- L2: 3MB vs 1.5MB
- L3: 16MB vs 9MB
This is another category that goes to the Ryzen 5 2600.
TDP – Power consumption
TDP stands for Thermal Design Power, or the maximum amount of heat that the processor’s cooling system is designed to dissipate. The lower the number, the less energy a CPU will consume.
On the other hand, a higher TDP (usually) means higher clock speeds and more energy consumption. You can expect more powerful CPUs to put out more heat, requiring more cooling power to handle high temperatures.
Here, our two CPUs both stand at 65W so there are no significant differences to be found.
Maximum operating temperature
At first glance, Ryzen 5 2600 and i5 9400F are designed to operate at similar temperatures.
When we dig a little deeper, however, we can see that the i5 9400F has a higher maximum operating temperature than Ryzen 5 2600 – 100oC compared to 95oC. This number represents the maximum temperature a CPU can withstand without problems like random resets.
In theory, this would mean that the i5 9400F is more stable, less prone to sudden issues.
The 5oC difference isn’t a big one but it’s just enough to win this category for i5 9400F.
RAM compatibility
The type of processor you choose will dictate the speed of RAM that fits best with your configuration.
AMD’s processors generally work better with faster RAMs so the Ryzen 5 2600 supports 2933MHz. The i5 9400F supports RAMs of up to 2666MHz, although you can go higher but you likely won’t see a big performance boost.
This might seem like another win for AMD but it’s a negligible difference since Intel’s processors aren’t affected by RAM speeds as much. Furthermore, it’s questionable to what extent RAM speeds even influence performance, especially when we’re comparing two different types of processors.
The bottom line: Ryzen 5 2600 recommends RAM of 2933MHz while i5 9400F recommends 2666MHz but this will hardly have a big effect on respective CPU’s performances.
Standout Features
Now that we’ve gone through the basic specs, let’s take a few moments to get into unique features that these two processors have to offer.
Ryzen 5 2600 can be overclocked?
One of the biggest knocks against the i5 9400F – especially in the mind of the avid gamer – is the fact that it can’t be overclocked. The CPU has a locked multiplier, preventing overclocking but promoting stability and longevity.
The Ryzen 5 2600, on the other hand, can be overclocked to a theoretical high of around 4.2 GHz. This is a significant increase from the base clock of 3.4 GHz and it even outperforms Intel’s Turbo Boost that, in the case of Intel’s 9400F, can reach up to 4.1 GHz.
Now, the long-term safety of overclocking is to be debated but if you’re a performance-focused user it’s definitely a plus to have that option.
Intel’s signature Turbo Boost
Intel’s alternative to overclocking is the Turbo Boost feature which allows you to increase single-core clock speed and improve the performance of applications that use only one core.

It’s comparable to overclocking but it’s not such a dramatic increase in performance and computing power since overclocking increases the clock speed of all cores. On the other hand, it’s not as damaging to the CPU’s long-term health since it’s 100% approved by the manufacturer.
With the i5 9400F, you can turn on the Turbo Boost and you’ll rarely ever have to turn it off.
Conclusion
We hope that our Ryzen 5 2600 vs i5 9400F comparison helped you learn the differences between these two powerful CPUs and clear up any possible confusion.
Overall, AMD’s Ryzen 5 2600 seems like the more powerful option with more threads, higher base clock speeds, and more cache memory. It’s more suited to productivity software, 3D rendering, Photoshop, and other apps that use multiple cores.
Intel’s i5 9400F has better single-core performance, making it marginally better for gaming. Still, the fact that it can’t be overclocked hurts it in the gaming department as well, especially when it comes to future-proofing.